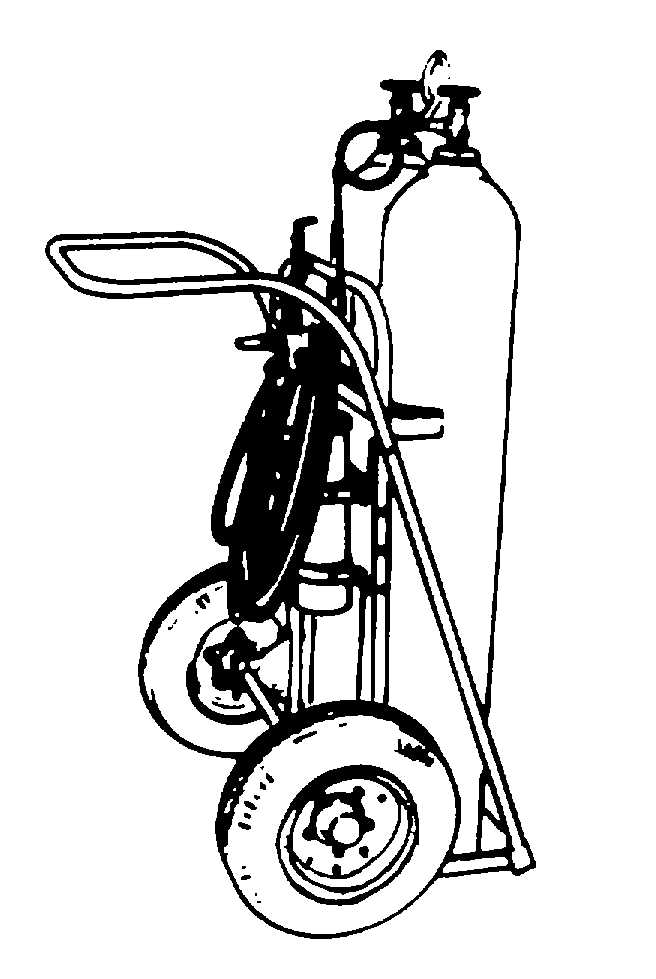
TM 1-1500-204-23-9
pressure from O psi to the operating pressure of the
aircraft system. The outlet pressure is read on a gauge.
(3)
Safety practices and procedures. The
following special precautions should be observed when
using the nitrogen servicing unit:
· Be careful not to knock over the high pressure
cylinders.
· Open all valves slowly.
· Do not exceed the aircraft system pressure or
quantity limit when servicing.
· Close all valves when moving the hand truck.
· Protect the fittings from contamination.
(4)
Operating
procedures.
Consult
the
applicable servicing unit and aircraft maintenance
manual for detailed instructions. The following general
procedures pertain to the operation of the nitrogen
servicing unit:
(a)
Position the cylinder so the hose is
at full length but not stretched.
Figure 9-17. Nitrogen Servicing Unit
(b)
Determine pressure of system to be
serviced.
(c) Open shutoff valve.
(d)
Set pressure regulator to correct
pressure.
(e)
Use hose and service system.
(f)
On completion of servicing, close
shutoff valve, set pressure regulator to 0 psi, and roll up
hose.
(5)
Inspection. The operator should perform
the following general inspections before using the
nitrogen
servicing
unit.
Detailed
inspection
requirements are in the applicable maintenance manual.
(a)
Cylinders. Check for security on
hand truck.
(b)
Hose and fittings. Check for
tightness and leaks.
(6)
Maintenance. Consult the applicable
maintenance manual for scheduled and preventive
maintenance requirements.
k.
Hoists. Hoist shown in figure 9-18, can be
categorized as fixed height. The fixed height apparatus,
normally referred to as a hoist, is made of a welded,
tubular steel, truss-type construction. The legs on the
hoists are spreadable to straddle the equipment and
provide balance while lifting. Casters provide mobility,
allowing two people to handle the positioning of the
hoist.
(1)
Purpose. Hoists are designed to remove
and replace aircraft components during scheduled and
unscheduled maintenance. These components include
engines, transmissions, propellers, rotor blades and
rotor hubs. The amount of weight that can be lifted is
determined by the type, size of construction and the size
of the cable.
(2)
Types. Two general types of hoists are
described in the following paragraphs.
(a)
Manually-operated. On this type of
hoist, the winch is operated by hand. It main benefit is
the ability to be used at locations where power is not
available. Typically, the hoist will lift 5,000 pounds over
20 feet. It must be used on a paved surface.
9-45