TM 1-1500-204-23-9
4
Using adapters and a hoist if
necessary, disassemble the engine as required.
5
After the engine is reassembled, it
may be removed from the engine maintenance stand by
reversing these procedures.
(e)
Inspection. The operator should visually
look at the welds for cracks and check the rail stops for
proper operation prior to using the stand.
(f)
Maintenance. Consult the applicable
maintenance manual for scheduled and preventive
maintenance requirements.
(g)
Sweeney
adapters.
Consult
the
applicable engine maintenance manuals for adapters
that can be used. TM 1-1500-204-23-9
(4)
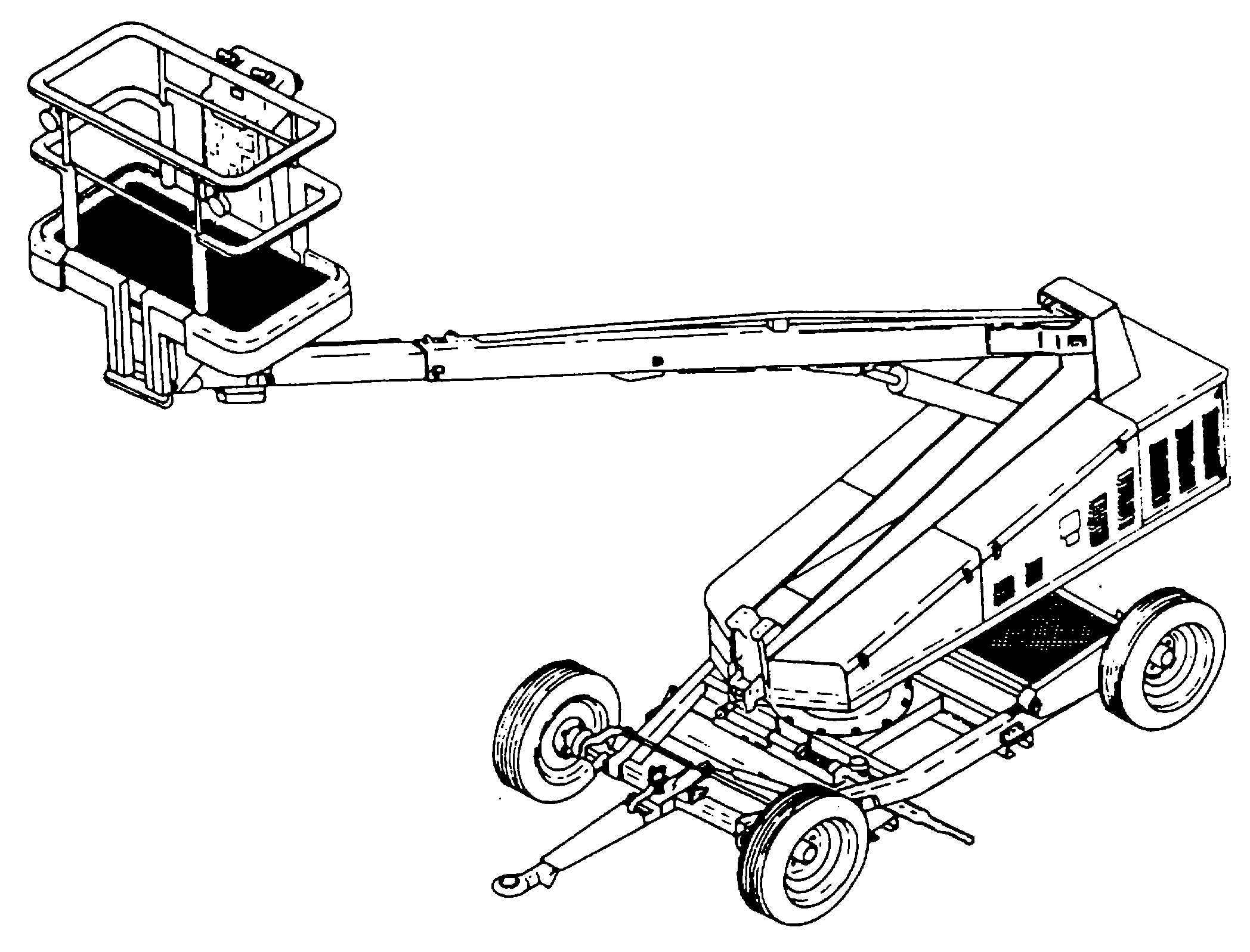
Self-propelled
elevated
maintenance
workstand. The Self-Propelled Elevated Maintenance
(SPEM) workstand, shown in figure 9-4, is driven by a
gasoline engine. The stand is self propelled at 2 mph
and can be driven from the workbasket.
(a)
Purpose. The SPEM stand is useful for
reaching areas of an aircraft that are not accessible
from a type B-1 or Type B-4A stand. The extendable
arm allows the workbasket to go over the aircraft and to
a height of 40 feet.
(b)
Principles of operation. The SPEM stand
is counterbalanced and propelled by a gasoline I engine.
The rear drive wheels are equipped with hydraulic
brakes that engage automatically when the drive control
is released. The front steering wheels have electric
brakes which are operated from the workbasket. The
turntable is hydraulically-operated and cab be rotated
350 degrees from the workbasket.
Figure 9-4. SPEM Stand
Change 2 9-29