TM 1-1500-204-23-4
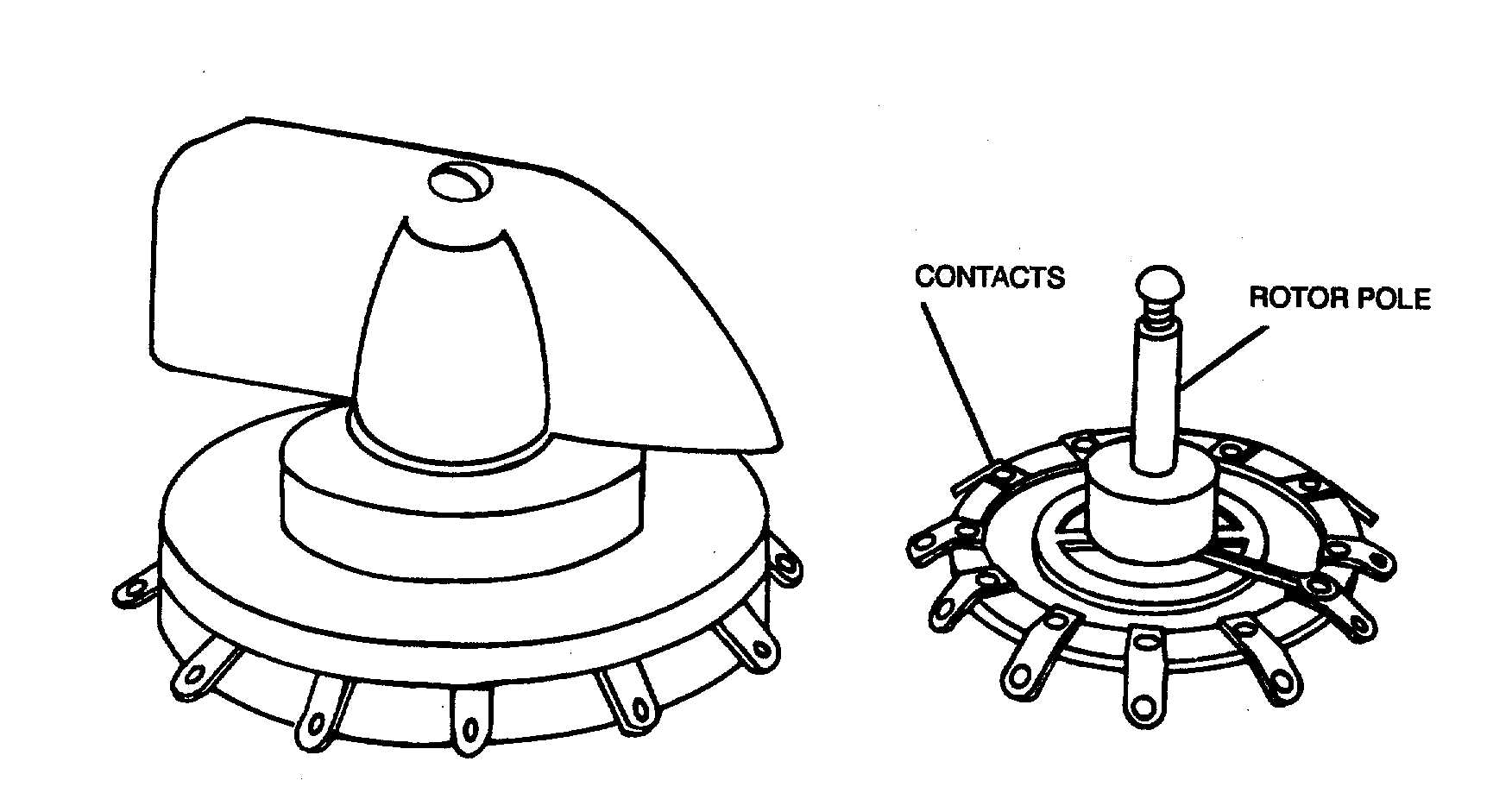
Figure 3-12. Rotary-Selector Switch
h. Motors. Motors transform electrical energy
into mechanical energy. Many aircraft devices, from the
starter to the automatic pilot, depend on motors for
mechanical energy.
(1) Types. Series, shunt, and compound
motors are the three basic types of dc motors. Induction
and synchronous motors are the two general types of ac
motors.
(2)
Inspection.
General
inspection
procedures for motors are as follows:
(a) Check the operation of the unit
driven by the motor in accordance with the instructions
covering the specific installation.
(b) Check all wiring, connections,
terminals, fuses, and switches for general condition and
security.
(c) Check brushes for condition,
length, and spring tension. Minimum brush lengths,
correct spring tension, and procedures for replacing
brushes are given in the applicable maintenance
manual.
(d) Inspect commutator for cleanness,
pitting, scoring, roughness, corrosion or burning.
(e) Check for high mica (if the copper
wears down below the mica, the mica will insulate the
brushes from the commutator).
WARNING
Drycleaning solvent is flammable
and solvent vapors are toxic. Use
P-D-680, Type II Solvent in a well-
ventilated area. Keep away from
open flames. Avoid prolonged
solvent contact with skin.
(f) Clean dirty commutators with a
cloth moistened with the recommended cleaning
solvent.
CAUTION
When polishing, never use emery
paper since it contains metallic
particles which may cause shorts.
Damage to equipment may occur.
When
using
compressed
air
reduce pressure to 30 psi or
lower.
(g)
Polish
rough
or
corroded
commutators with fine sandpaper (000 or finer) and blow
out with compressed air.
(h) Inspect all exposed wiring for
evidence of overheating.
(i) Adjust and lubricate the gearbox, or
unit which the motor drives, in accordance with the
applicable maintenance manual covering the unit.
Change 3 3-18