TM 1-1500-204-23-6
NOTE
Care should be taken to prevent dissimilar metal corrosion.
•
When a self-locking feature cannot be provided in externally or internally threaded part.
•
When a cotter pin cannot be used to prevent rotation of an internally threaded part with respect to an
externally threaded part
•
When lockwire cannot be used to prevent loosening of threaded parts.
•
When fastening is not used for fabrication of primary structure.
•
When loosening of threaded parts would not endanger the safety of aircraft to personnel
•
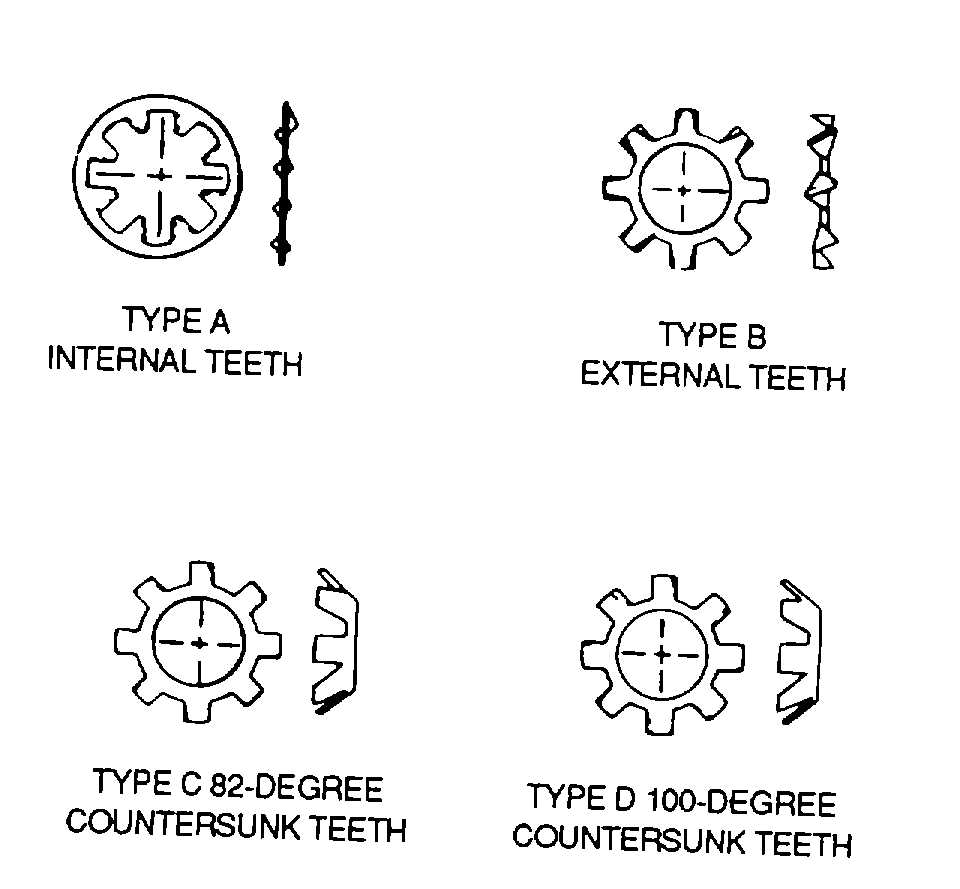
When corrosion, encouraged by gouging of aluminum or magnesium alloys by edges of teeth on
MS325333, MS35335, MS35336, and MS35790 washers, would not cause malfunctioning of parts being
fastened together. Corrosion of dissimilar metals may be reduced by installing MS35333, MS35335,
MS35336, and MS35790 washers wet with primer, MIL-P-23377.
Figure 2-31. Teeth-Type Lockwashers
c. High Tensile Special Washers. Taper pin, high tensile, countersunk, and preload indicating special washers are
identified in figures 2-32 through 2-35.
(1)
Taper pin washers. Use a taper pin or dished washer, AN975, in conjunction with threaded taper pin,
AN386 install washer under nut AN320 to effect adjustment where a plain washer would cause distortion.
(2)
High tensile washers.
Use a high tensile washer, MS20002, in conjunction with high tensile internal
wrenching bolts, MS2004 through MS20018. A Type C washer is countersunk to seat the bolt head shank radius, and a
plain type washer is used under the nut Plain and countersunk washers, MS20002 and MS20002C, are heat-treated to
125,000 to 145,000 psi.
(3)
High Tensile Countersunk washers.
Countersunk washers, commonly called dimpled washers, are for
use with 100-degree flat-head screws, or rivets, to provide reinforced, low-profile attachments in such locations as fillets
and other fairing installations. Identify countersunk washers by part number. Examples: A3236-0.012 (No. 6 screw),
A31350-0 017 (No. 8 screw), A3235-0.020 (No. 10 screw).
CAUTION
Damage to preload indicating washer may occur if the nut is
overtightened
Figure 2-32. Taper Pin Washer
2-36