TM 1-1500-204-23-6
a. Screw Heads. Aside from head style, such as countersunk, brazier-head, and round head, various type slots or
recesses are provided for the screwdriver The Phillips or Frearson recessed head is optional on several type screws For
proper performance, a Phillips screwdriver should be used with Phillips recessed-head screws, and a Frearson
screwdriver with Frearson recessed-head screws. The Phillips and the Frearson screwdrivers are not interchangeable.
Mutilation of the screw head can be prevented by using the proper type and size screwdriver
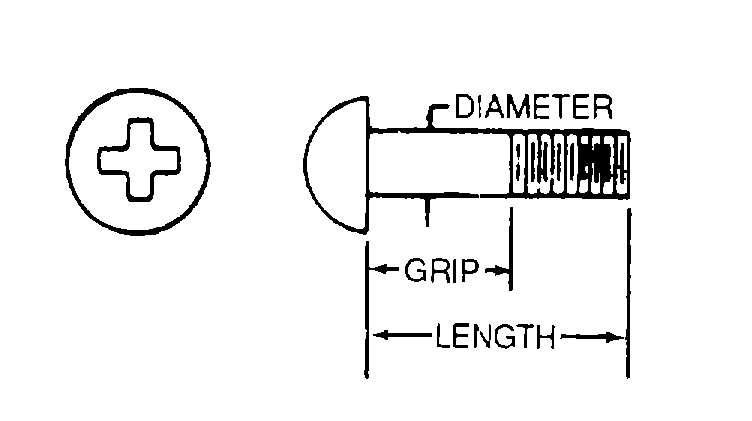
b. Length Measurement. Determine length of screws as follows:
(1)
Measure flat-head screws from top of head to end of thread.
(2)
Measure all other screws from bottom of end of thread as shown in figure 2-36.
NOTE
Lengths will be specified in 1/16-inch differences up to 1 12 inches; 1/8-
inch differences from 1 1/2 inches to 3 inches, and 1/4-inch differences
for all lengths over 3 inches.
c. Structural Screws. Structural screws are used in the primary structure of aircraft as structural bolts or rivets are
used These screws are fabricated from a material with a high tensile strength and differ from structural bolts only in the
type of head. They have a definite grip and the same shear strength as the equivalent size bolt. Examples include:
MS24694 flat-head screws, and NAS220 through NAS235 brazier-head screws.
(1)
Flat countersunk-head screws. The MS24694 (100-degree) flat countersunk head screw, as shown in
figure 2-37, is used in countersunk holes where a flush surface is necessary.
(2) Brazier-head screws. The NAS220 through NAS235 brazier-head screws, as shown in figure 2-36, have
the same characteristics as MS24694 flat-head screws, except for the difference in the heads The NAS80 (100-degree)
close tolerance countersunk bolt is similar to the MS24694 (100-degree) flat-head screw
Figure 2-36. Structural Screw
(3)
Pan-head screws. The MS27039 pan-head structural screw is used where the raised head is not
objectionable The pan-type head provides a large contact area
NOTE
Screws are marked with a code to identify their physical characteristics
and contents. Refer to table 2-1 for these code markings.
d
Machine Screws. The main type of machine screws are round head, countersunk, and fillister head
(1)
Round-head screws. Round-head screws, MS35206, MS35214, MS35218, MS51957, and MS35207,
MS35215, MS35219, MS51958 are general purpose screws available in low carbon steel, brass, and corrosion-resistant
steel. The MS35206, MS35214, MS35218, MS51957 are coarse thread screws and MS35207, MS352'15, MS35219,
MS51958 are fine thread Both have recessed heads and a class 2 thread fit The AN508 brass screw is designed for
electrical use only, and is available only with a slotted head.
(2)
Countersunk screws. The MS35190, MS51959, and MS35199, MS35203, MS51960 countersunk
screws correspond to round-head screws, MS35206, MS35214, MS35218, MS51957, and MS35207, MS35215,
MS35219, MS51958, in material and application. The countersunk type, as shown in figure 2-38, is a low carbon steel
screw.
2-38