TM 1-1500-204-23-9
(a) Place the blade or tongue of the square
against the side of the material with the square tilted
slightly so the blade or tongue of the square extends
across the work.
CAUTION
Do not mark on any metal surface with a
graphite pencil. Graphite is cathodic and
will establish the basic for galvanic
corrosion.
(b) Mark a line across the work using a
marking pencil, MIL-P-83953.
(2) Combination square. The uses of the
various parts of the combination square are described in
the following paragraphs.
(a) Center head. The center head can be
used to locate and mark the diameter of a cylinder.
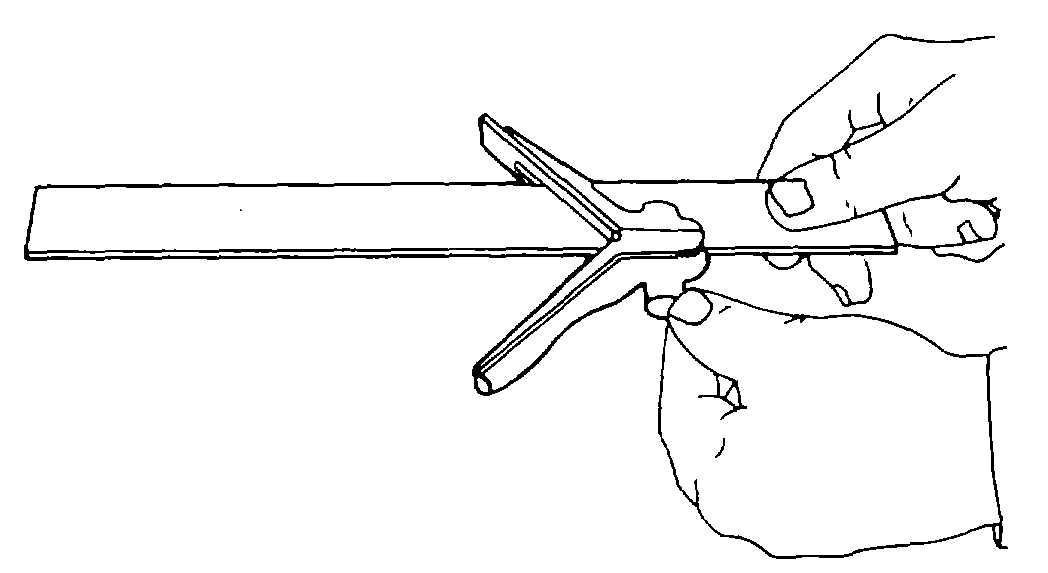
1 As shown in figure 3-14, slide the
center head on the rule and fasten by tightening the
setscrew.
Figure 3-14. Setting the Center Head
CAUTION
Do not mark on any metal surface with a
graphite pencil. Graphite is cathodic and
will establish the basic for galvanic
corrosion.
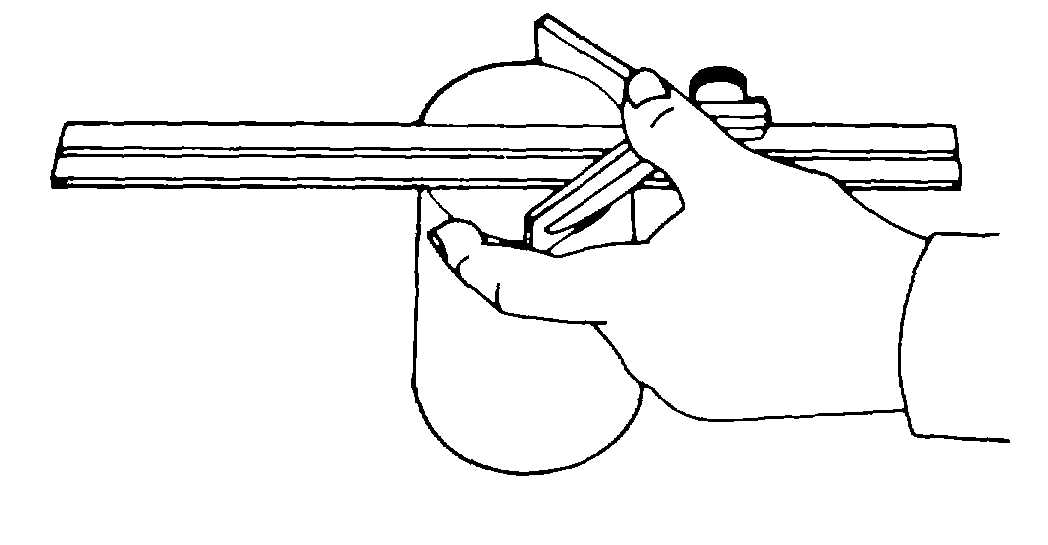
2 Push the center head against the
cylinder, as shown in figure 3-15.
Figure 3-15. Locating Diameter of Cylinder
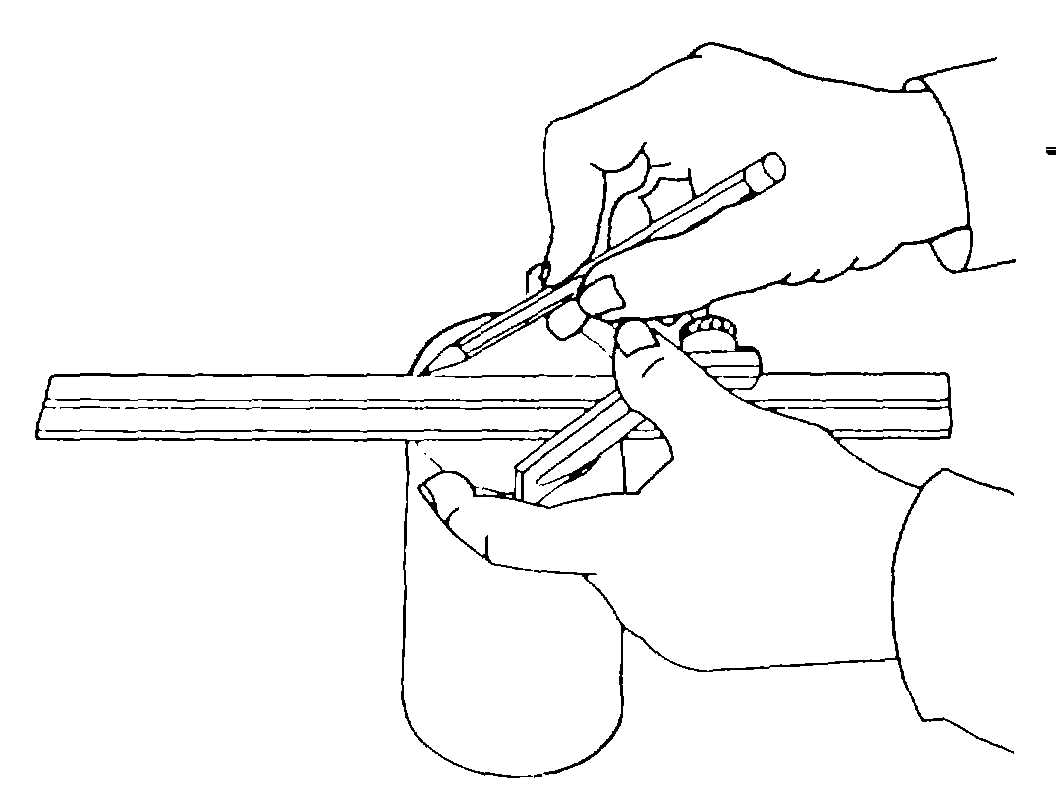
3 Mark the diameter on the cylinder
using a marking pencil, MIL-R-83953, by drawing a
straight line along the inside edge. Make sure the
square does not slip while marking. This is shown in
figure 3-16.
Figure 3-16. Marking Diameter of Cylinder
(b) Protractor head. The protractor head
can be used to determine the angle of a previously
marked line.
1 Slide the protractor head on the rule
as shown in figure 3-17, and tighten the setscrew.
2 Loosen the protractor adjustment
screws so the protractor may be pivoted about the rule,
as shown in figure 3-18.
3-6