TM 1-1500-204-23-9
(5) Bevel protractor. The bevel protractor is
used much the same as the protractor head of the
combination square.
c. Care of Squares. Squares can be maintained by
observing some common precautions:
(1) Make sure squares are kept clean.
(2) Apply a light coat of oil to all metal surfaces
after using.
(3) If a stock is loose, replace the square.
False measurements can be made if the stock is able to
move slightly.
3-7. Dividers. Dividers are tapered steel picks hinged
together on the blunt end. They are used to scribe arcs
and circles and to transfer measurements when laying
out work. They are also used to transfer or compare
measurements directly from a rule.
a. Types. The most common types of dividers are
the spring divider and the wing divider, which are
described in the following paragraphs.
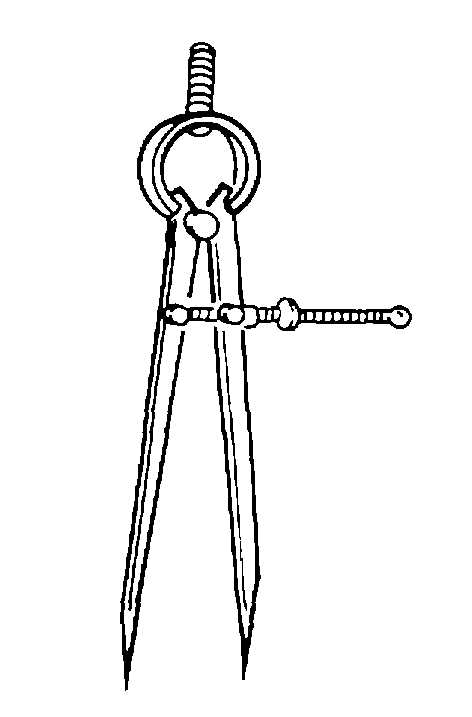
(1) Spring divider. A spring divider consists of
two sharp points at the end of straight legs, held apart
by a spring and adjusted by means of a screw and nut.
The spring divider is available in sizes from 3 to 10
inches in length. It is shown in figure 3-21.
Figure 3-21. Spring Divider
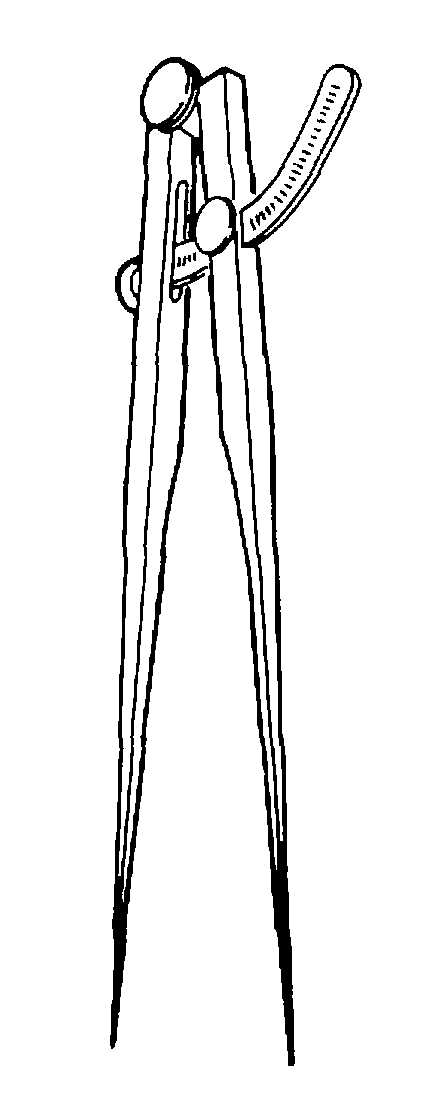
(2) Wing divider. A wing-type divider has a
steel bar that separates the legs, a lock nut for setting a
rough measurement, and an adjustment screw for fine
adjustments. The wing-type divider is available in 6, 8,
and 12 inch lengths, and is shown in figure 3-22.
Figure 3-22. Wing Divider
b. Use of Dividers. Dividers can be used to scribe a
circle by using the following procedures (see figure 3-
23):
(1) Set the desired radius on the dividers using
the appropriate graduations on a rule.
(2) Place the point of one of the divider legs on
the point to be used as the center.
(3) Lean the dividers in the direction of
movement and scribe the circle by revolving the
dividers.
c. Care of Dividers. The following procedures
describe the care and maintenance of dividers:
(1) Keep dividers clean and dry.
(2) Store dividers where they will not become
bent or broken.
3-8