TM 1-1500-204-23-1
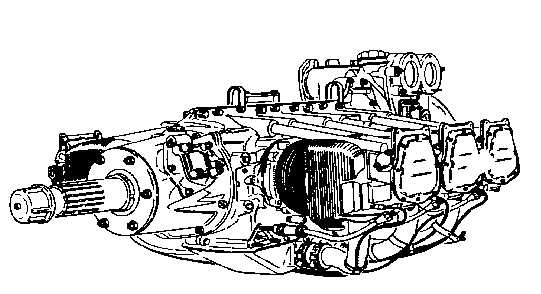
Figure 7-2. Opposed-Type Engine
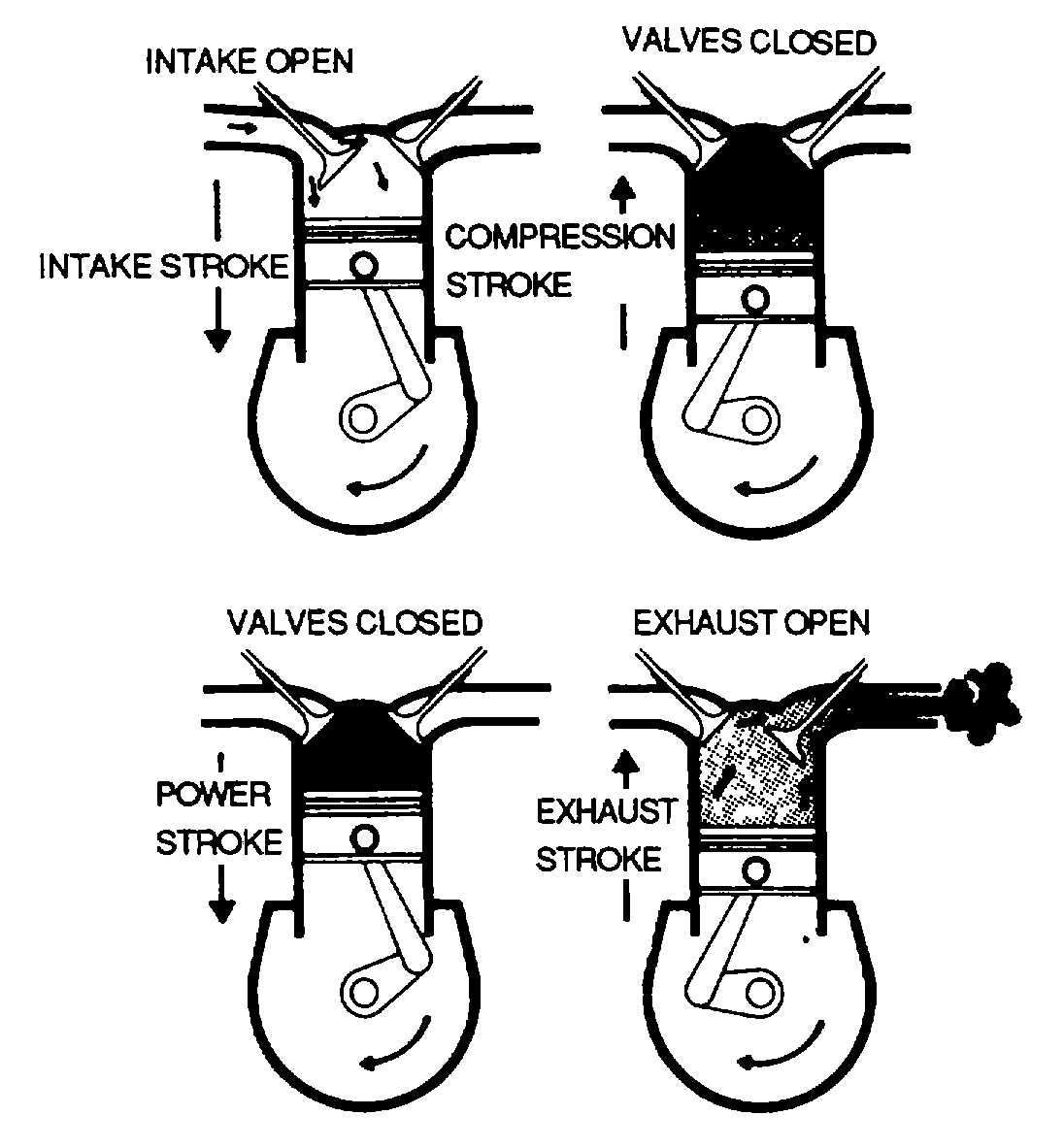
Figure 7-3. Reciprocating Engine Operating
Cycle (Four-Stroke)
(1)
Types. Opposed-type and radial-type
engine crankcases are described in the following
paragraphs.
(a)
Opposed-type crankcases. The
crankcases used on engines opposed vary in form but in
general they are approximately cylindrical. One or more
sides are surfaced to serve as a base to which the
cylinders are attached by means of capscrews, bolts, or
studs. The crankshaft is carried in a position parallel to
the longitudinal axis of the crankcase and is generally
supported by a main bearing between each throw. See
figure 7-4.
(b)
Radial-type crankcases. Radial-
type engine crankcases, as shown in figure 7-5, vary in
size and number of sections. Four common sections are
described by the following paragraphs.
1
Nose section. The nose
section is usually made of an aluminum alloy and is
fastened to the power section by studs and nuts or caps
and screws. Most nose sections support the propeller
thrust bearing, propeller governor drive shaft, and the
propeller reduction gear assembly. Various other engine
accessories are sometimes attached.
7-2