TM 1-1500-204-23-1
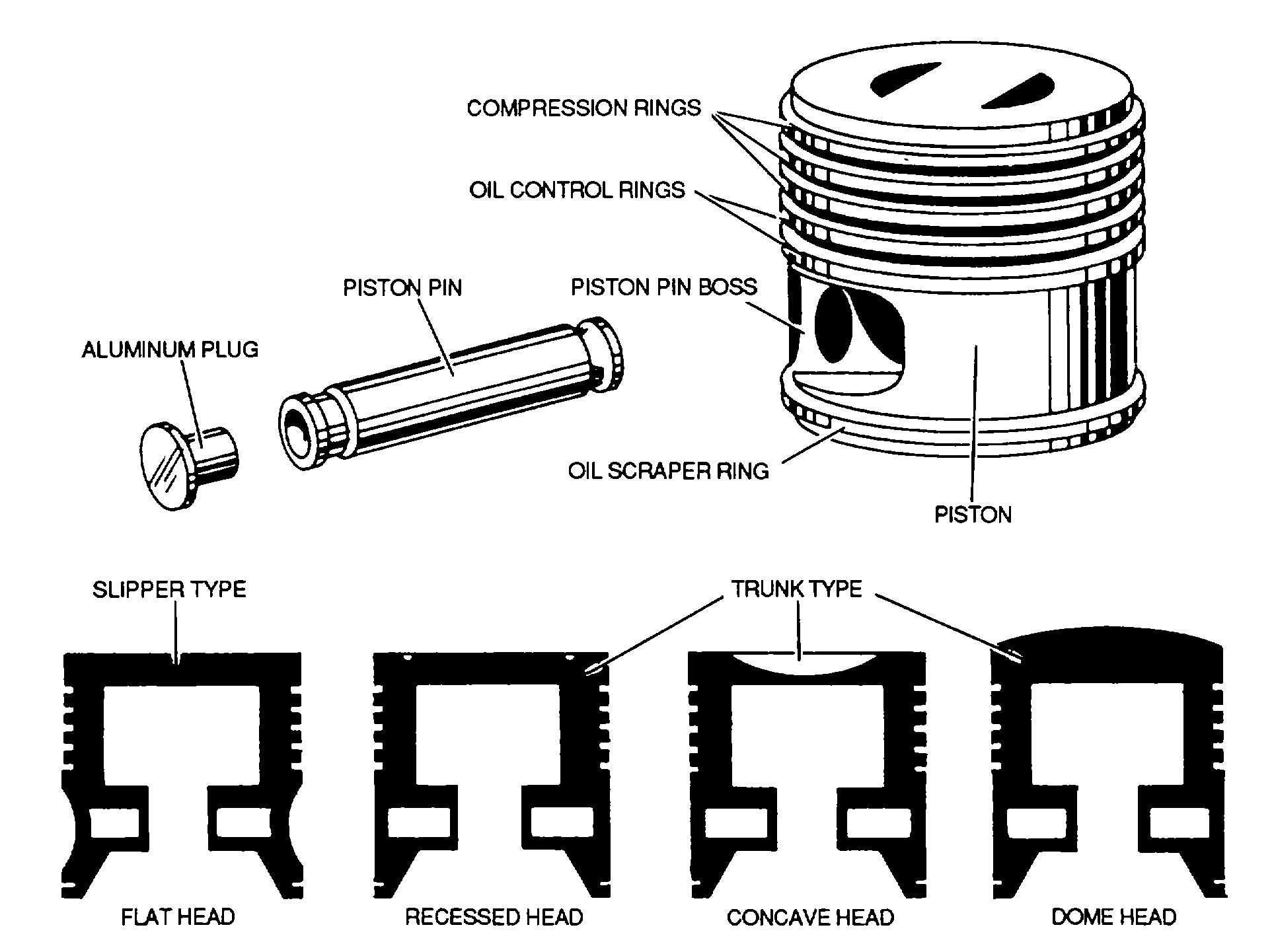
Figure 7-10. Piston, Pin, and Ring Assemblies
(2)
Maintenance.
Cylinder
maintenance
procedures are explained in the following paragraphs. All
openings to a cylinder must be completely closed and
sealed during the compression and power strokes In order
to maintain proper compression and thus prevent power
loss. The requirements for proper sealing are: good
piston rings with no leakage between pistons and walls of
the combustion chamber, tightly closing. Intake and
exhaust valves, and proper valve timing to ensure highest
efficiency obtainable when engine is operating at its
normal rpm. Compression loss at any of these points
results in reduced engine efficiency. Early detection and
correction of these faults will prevent cylinder breakdown.
Since most engine difficulties can be traced to a small
number of cylinders, engine malfunction can be corrected
by locating defective cylinders and taking corrective
action. Each phase of cylinder operation, such as
compression, fuel mixture, or ignition, must function
properly to maintain cylinder compression.
NOTE
Dark stains adjacent to the cylinder
head and barrel seam must not be
misinterpreted.
During
engine
operation,
the
high
temperature
thread lubricant used during barrel
and head assembly may be extruded
at
the
seam
leaving
a
heavy
discoloration. Such a condition is In
no
way
hazardous
to
engine
operation, therefore, verification of
cylinder failure must be by means
other than stains alone. A cylinder
should
be
removed
for
head
separation only if it displays visible
damage and/or fails the normal
compression test.
7-8