TM 1-1500-204-23-1
oll-flltering screens, Cuno filters, and other items of
accessory equipment. In some aircraft powerplants, the
cover for the supercharger rear housing is made of an
aluminum-alloy or a magnesium-alloy casting in the form
of a heavily ribbed plate that provides the mounting pads
for the accessory units; but in other powerplants, the
housings for the accessory units may be mounted directly
on the rear of the crankcase. Regardless of the
construction and location of the accessory housing, it
contains the gears for driving the accessories which are
operated by engine power.
(2)
Maintenance. Crankcase maintenance
consists of inspection for cracks, warping, damage to
machined surfaces, warn bushings and bearing bores,
loose or bent studs, corrosion damage, and other
conditions which may lead to failure in service Refer to
the applicable maintenance manual
NOTE
Two-piece
crankcases
are
manufactured with matched parts;
therefore
it
one
half
must
be
discarded, the entire crankcase is
replaced
b.
Crankshafts. The crankshaft transforms the
reciprocating motion of the piston and connecting rod into
rotary motion for turning the propeller It Is a shaft
composed of one or more cranks or throws The parts are
the main journal, crankpln, crank cheek or crank arm, and
the
counterweights
and
dampers
The
following
paragraphs describe crankshaft types and general
maintenance.
(1)
Types. Opposed-type and radial-type
engine crankshafts are described in the following
paragraphs.
(a)
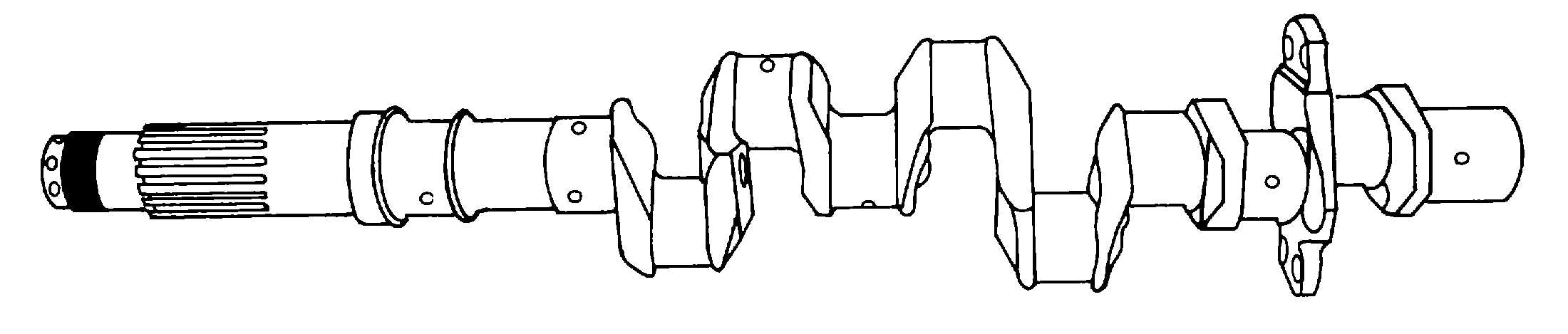
Opposed-type crankshaft. A typical
six cylinder opposed-type crankshaft is shown in figure 7-
6. This crankshaft is a one-piece, six-throw, 60-degree
crankshaft machined from an alloy-steel (SAE 4340)
forging. The crankpins and main bearing journals are
ground to close limits of size and surface roughness.
(b)
Radial-type crankshaft. Figure 7-7
shows a single-throw 360-degree crankshaft used on
single-row radial engines. It may be of single-piece or
two-piece construction with two main bearings (one on
each end) This single piece crankshaft must be used with
a master rod having the large end split
(2)
Maintenance. Crankshaft maintenance is
critical to safe engine operation. The dimensions of the
journals, the balance, and the alignment of the shaft must
be within tolerances when inspected and measured. The
crankshaft should be inspected by the magnetic methods
to detect flaws and defects. Refer to the applicable
maintenance
manual
for
specific
maintenance
procedures and tests.
Figure 7-6. Opposed-Type Crankshaft (Six-Cylinder) (Six-Throw)
7-4