TM 1-1500-204-23-6
•
Bolts, studs, and screws of 5/16-inch diameter and over with cotter pin holes may be used with nonmetallic insert
self-locking nuts, provided the cotter pin holes are free from burrs. Burrs tend to tear the nonmetallic insert,
rendering it unsatisfactory as a locking device.
•
Bolts, studs, and screws of 1/4-inch diameter and under with cotter pin holes may be used with nonmetallic insert
self locking nuts in an emergency. These nuts shall be replaced as soon as possible with the specified type.
•
Do not use bolts, studs, and screws with rough ends and damaged threads
•
Do not subject nonmetallic self-locking insert nuts to temperatures in excess of 250
°F (121°C).
•
Do not run a thread-cutting tap through a nonmetallic insert self-locking nut, as this will destroy the self-locking
properties.
(2) Application Self-locking nuts are used in conjunction with specially fabricated parts, or they are fabricated for
specific purposes Various applications of self-locking nuts include use as plate nut, channel assemblies, and for engines
and accessories. Except as stated herein, the various applications of self-locking nuts are subject to the same general
guidelines described previously for all-metallic and nonmetallic self-locking nuts.
(a)
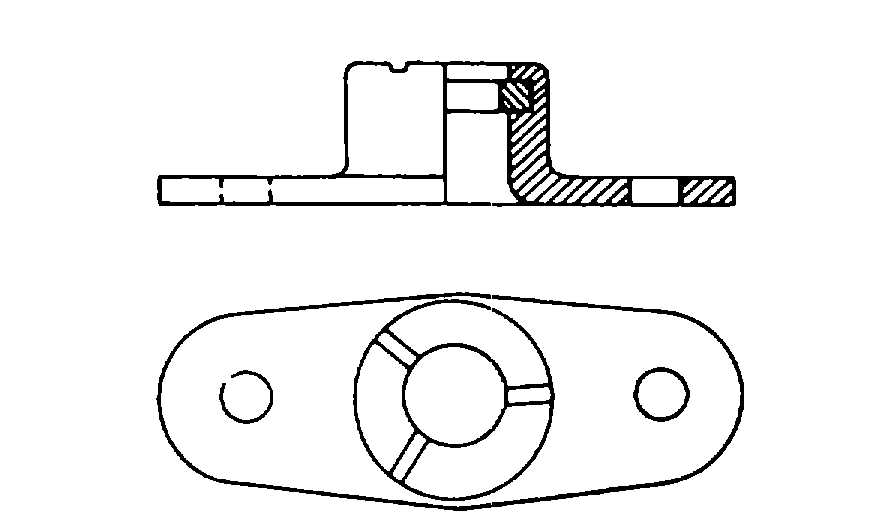
Plate nuts. Plate nuts, also called anchor nuts, are shown in figures 2-16 through 2-18 These self-
locking nuts, MS21047, MS21048, and MS21078, are used to give flexibility in locations where the self-locking feature is
required for use. These nuts must be handled and installed carefully to prevent them from being deformed. Bases are
countersunk for flush mounting, plain for modified welding, and equipped with ribs for projection welding (figure 2-18) The
floating anchor nut (figure 2-17) is designed so the plate will hold the nut, with a sideways floating feature, approximately
centered over a bolt or screw hole. When properly tightened, the nut rests firmly against its holder Floating anchor nuts
are for nonstructural usage and should be used in locations where the temperature does not exceed 250
°F (121°C).
Bolts and screws 1/4 inch diameter and smaller with cotter pin holes should not be used in all metal plate nuts Self-
locking plate nuts may be reused as long as they meet the minimum breakaway torque requirements of table 2-8.
NOTE
Plate nuts, installed with projection welds, will be removed by drilling out
the welds in such a manner that a standard drilled plate nut can be used
for replacement.
(b) Channel assemblies. Channel assemblies with only a few rivets, as shown in figure 2-19, permit attachment of
numerous self-locking nuts. The channels are track-like bases with regularly spaced removable or nonremovable nuts.
The removable-type channel assembly carries a floating nut which can be snapped in or out to simplify removal of
damaged nuts. Self-locking nuts may be reused as long as they meet the minimum breakaway torque requirements of
table 2-8. Replace the individual damaged nuts or the channel assembly as appropriate.
(c)
Engines and accessories Self-locking nuts applicable only to engines and accessories are used as
follows
1 Secure rocker box covers on air- cooled engines with self-locking nuts.
2 Use self-locking nuts where specified by manufacturer on his assembly drawings, part lists, and bills of
materials, or where their use is shown in the applicable illustrated parts breakdown manual for a particular type and
model of engine or accessory.
3 Do not use No. 10 or 1/4-inch size self-locking nuts with drilled studs
4 See figure 2-20 for example of an engine self-locking nut.
Figure 2-16. Self-Locking Plate Nut
2-28