TM 1-1500-204-23-6
Figure 2-52. Cotter Pins
2-8.
Rivets. Refer to Chapter 7, TM 1-1500-204-2310, for the application of common rivets and special rivets.
a. Common Solid Shank Rivets. Common solid shank rivets are identified by head style and markings.
(1)
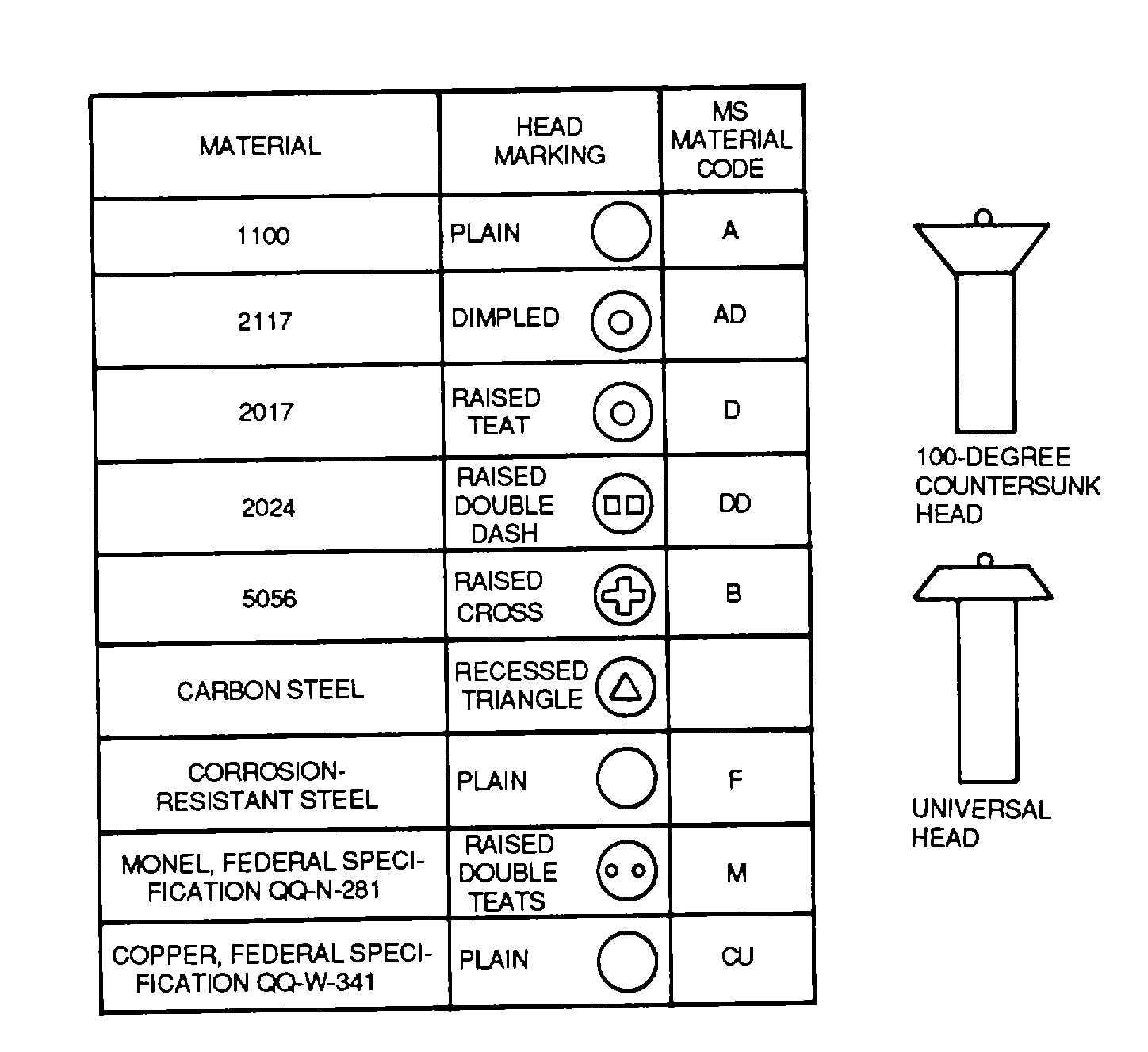
Identification. General identification information for standard MS rivets is shown in figure 2-53
(2)
Head styles. The universal head and countersink head are the two main head styles. Each is explained
in the following paragraphs.
(a)
Universal head.
Use universal-head rivets in interior and exterior locations. Use them in interior of
aircraft except when clearance for adjacent members is required. Use them on exterior aircraft surfaces where flush
riveting is not required. This avoids the necessity of dimpling or countersinking.
(b)
Countersunk head. Use countersunk head rivets on exterior surfaces to provide a smooth aerodynamic
surface or to develop a high shear strength, as in case of dimpled sheets. The dimpled joint and the protruding head
riveted joint are stronger than the machine countersunk rivet joint. Machine countersinking, with dimpled outer sheet, still
allows the sheet to carry a shear load comparable to dimpling. Use these rivets in aircraft interior where universal-head
rivets cannot be used.
Figure 2-53. Rivets
2-45