TM 1-1500-204-23-9
(3)
Hardness. Hardness of a grinding wheel
is a measurement of the ability of the bond to retain the
abrasive grains in the wheel. Grinding wheels are said
to have a soft to hard grade, which indicate the wheel
has a large amount of bond (hard) or a small amount of
bond (soft).
c.
Types of Grinding Wheels. The selection of
grinding wheels for precision grinding can be discussed
generally in terms of such factors as the physical
properties of the stock to be ground, the amount of stock
to be removed (depth of cut), the wheel speed and work
speed, and the finish required. Selection of a grinding
wheel is determined by considering one or more of
these factors. The following paragraphs describe the
types of wheels which can be used to grind metals with
certain general qualities.
(1)
Wheel abrasive type. An aluminum oxide
abrasive is most suitable for grinding carbon and alloy
steel, high speed steel, cast alloys and malleable iron. A
silicon carbide abrasive is most suitable for grinding
nonferrous
metals,
nonmetallic
substances,
and
cemented carbides.
(2)
Wheel coarseness. Generally, the softer
and more ductile the substance being ground, the
coarser the grain selected should be. Also, if a large
amount is to be removed, a coarse grain wheel is
recommended (except on very hard objects). If a good
finish is required, a fine grain wheel should be used.
(3)
Wheel hardness. For soft metals, small
depth of cut, or high work speed, use a soft grade wheel.
If the machine you are using is worn, a harder grade
may be necessary to help offset the effects of wear of
the machine. Using a coolant also permits the use of a
harder grade of wheel.
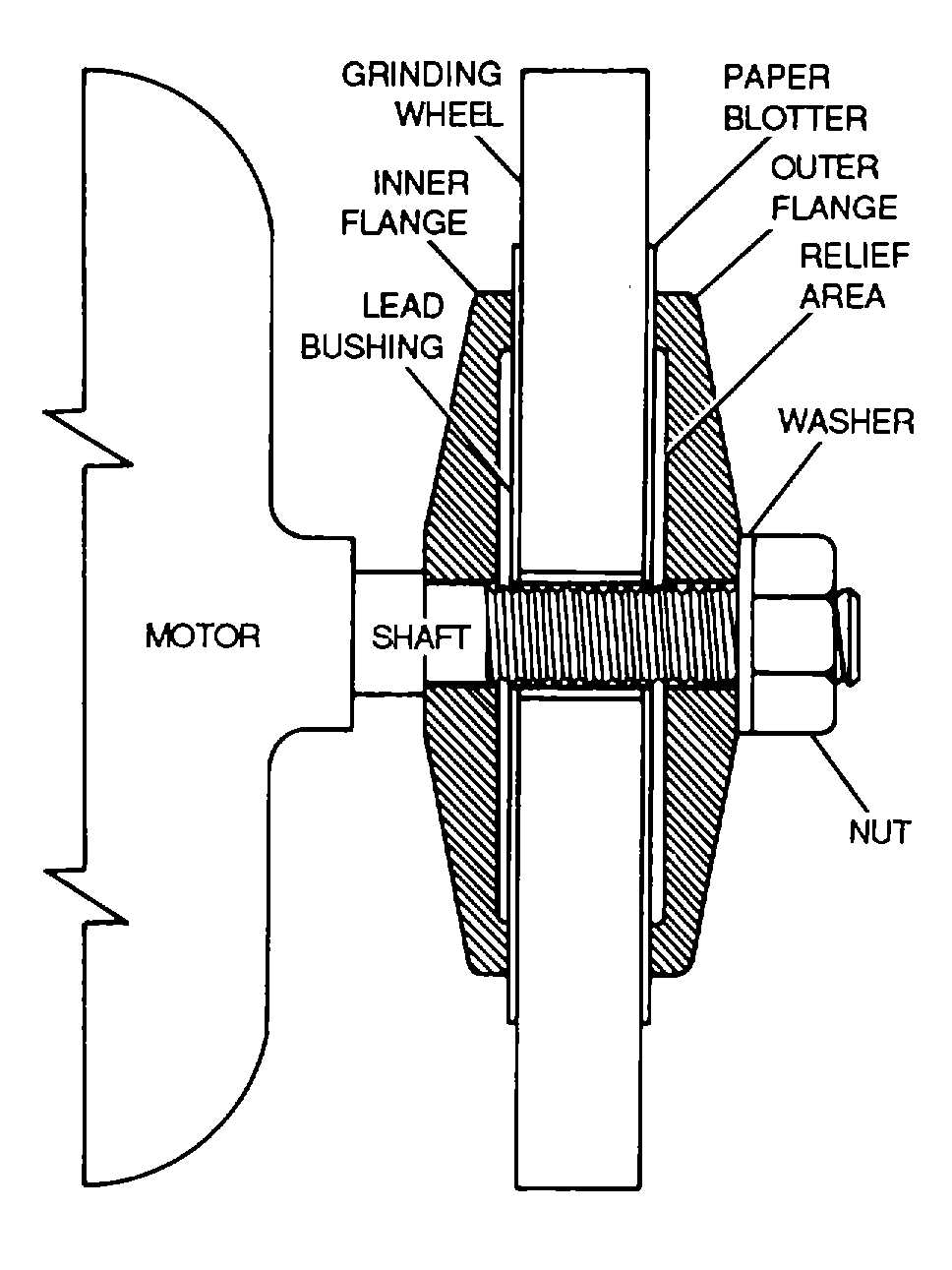
d.
Wheel Installation. The wheel of a grinder must
be properly installed. If it is not, the wheel may operate
improperly, and an accident may occur. Install a grinder
wheel as follows (see figure 6-5):
CAUTION
Do not use a metallic object for testing
the soundness of a grinding wheel. The
wheel may crack and disintegrate at any
time.
(1)
Test the wheel for soundness by tapping it
lightly with a piece of hard wood. A good wheel gives
out a clear, ringing sound when tapped. If the wheel is
cracked, a dull thud will be heard.
Figure 6-5. Grinding Wheel Installation
(2)
Ensure that the shaft and flanges are
clean and free of grit and old blotter.
(3)
Install the inner flange on the shaft.
NOTE
The blotter thickness for paper must be
no thicker than 0.025 inch. A leather or
rubber blotter must be no thicker than
0.125 inch.
(4)
Place a blotter on the shaft and up against
the flange to ensure even pressure on the wheel, and to
dampen the vibration between the wheel and the shaft.
CAUTION
Never force the wheel on the shaft. This
may cause the wheel to crack, or be out
of alignment.
6-4