TM 1-1500-20423-9
(a)
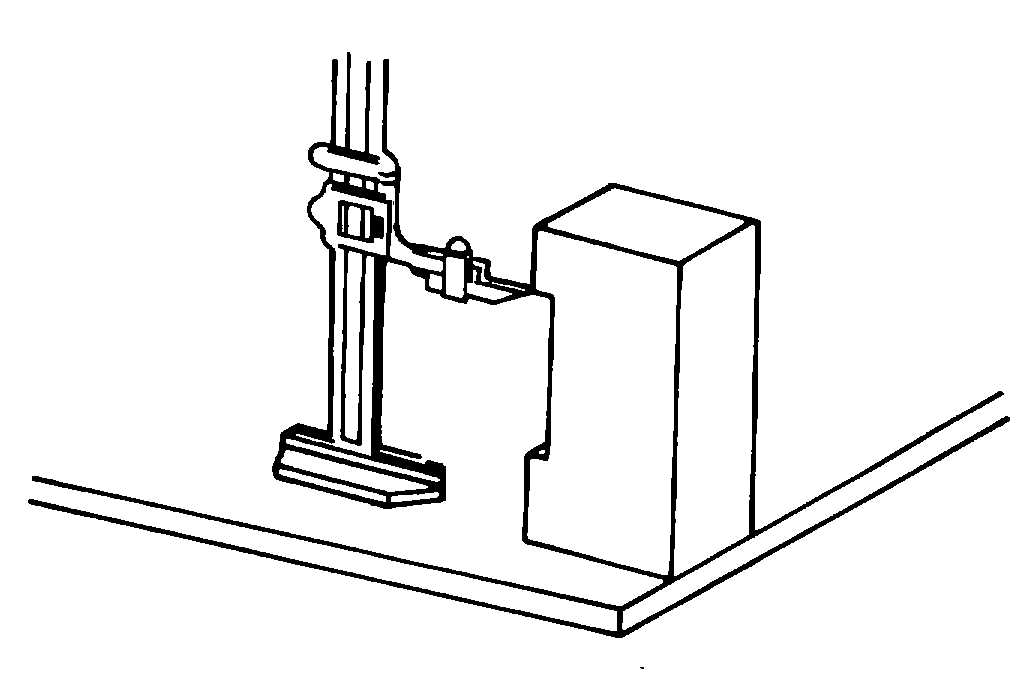
Place the vernier depth gauge over the
slot, as shown in figure 3-50.
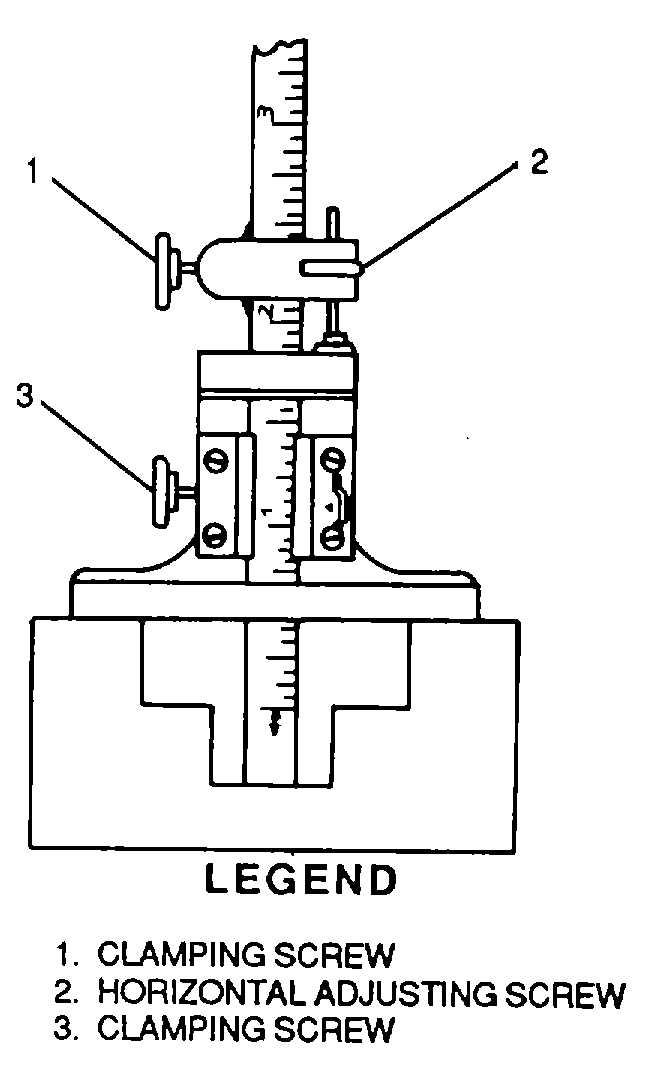
Figure 3-50. Using a Vernier Depth Gauge
(b)
With clamping screws (1) and (3) loose,
slide the rule down into the slot being measured until it
is almost in contact.
(c)
Tighten clamping screw (1) to make the
horizontal adjusting screw (2) operative.
(d)
With the horizontal adjusting screw (2),
adjust the rule to the first sense of contact between the
end of the scale and the bottom of the slot.
(e)
Secure the setting with clamping screw
(3).
(f)
Read the scale in accordance with
paragraph 3-8c.
(3)
Micrometer depth gauge. To measure the
depth of a hole or slot with even more accuracy than is
possible with either the vernier or the rule depth gauges,
proceed as follows:
(a)
Place the micrometer depth gauge over
the slot.
(b)
Adjust the thimble until the contact of the
spindle causes the ratchet stop to slip.
(c)
Remove the micrometer from the work
and read in accordance with paragraph 3-9.
NOTE
If extension rods are used, the total depth
reading will be the sum of the length of
the
rods
plus
the
reading
on
the
micrometer.
c.
Care of Depth Gauges. Observe the following
practices for the care and upkeep of depth gauges:
(1)
Coat all metal parts of depth gauges
with a light coat of oil to prevent rust.
(2)
Carefully store depth gauges in
separate containers provided by the manufacturer.
(3)
Keep graduations and markings
clean and legible.
(4)
Do not drop any depth gauge.
Small nicks and scratches can result in inaccurate
measurements.
3-12. Height Gauges. Height gauges are used to
measure the vertical distance of a point from a surface,
as shown in figure 3-51.
Figure 3-51. Typical Height Gauge
3-23