TM 1-1500-204-23-9
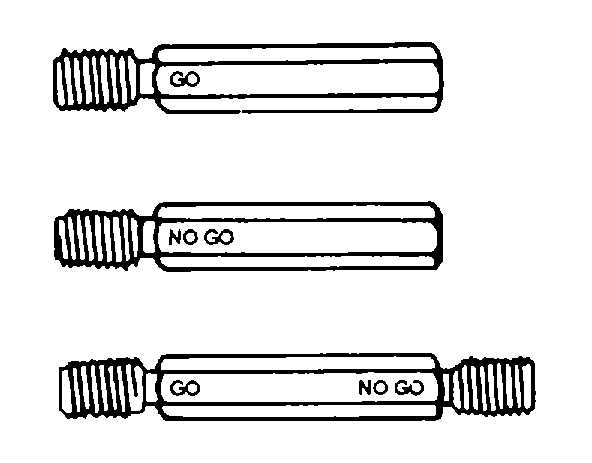
Figure 3-54. Plug Gauges
(2)
NO GO gauge. An internal thread within
limits must not accept the NO GO gauge past 1 1/2
turns.
b.
Care. Ensure that plug gauges are carefully
handled, as the threads are machined to within very fine
tolerances, and any damage will alter the accuracy of
the measurements. Observe the following additional
practices for the care and upkeep of plug gauges:
(1)
Coat metal parts with a light film of oil to
prevent rust.
(2)
Store gauges in separate containers
provided by the manufacturer.
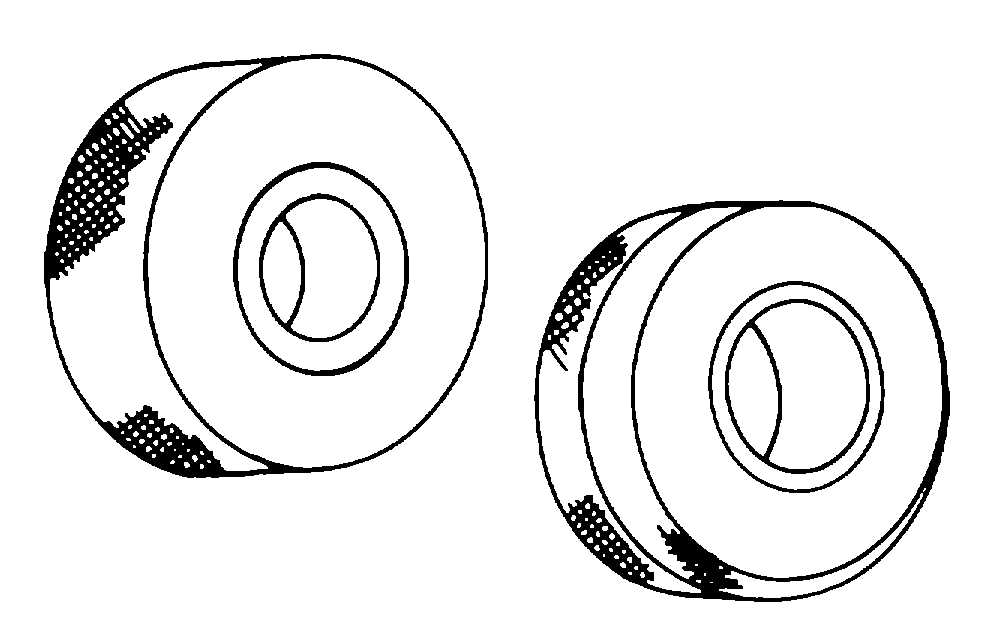
3-15. Ring Gauges. Ring gauges, shown in figure 3-
55, are used as standards to determine whether or not
one or more dimensions of a manufactured post are
within specified limits. They are nonadjustable, and
therefore called fixed gauges.
a.
Description. The ring gauge is an external
gauge of circular form. For sizes between 0.059 and
0.510 inch, ring gauges are made with a hardened
bushing pressed into a soft body. The thickness of the
gauge ranges from 3/16 to 1 5/16 inches. Ring gauges
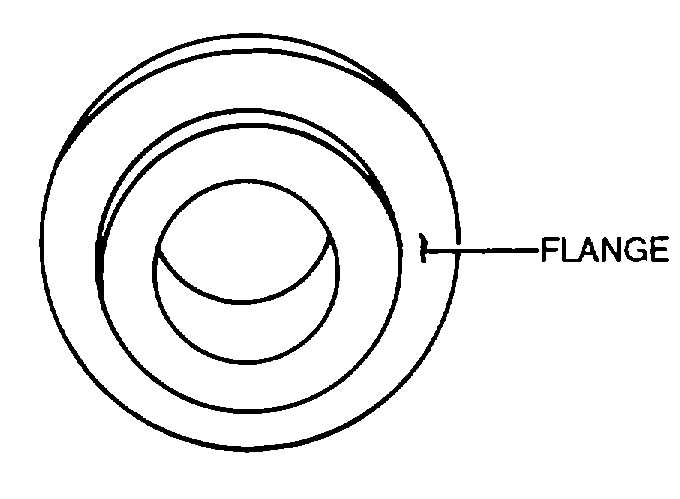
made for diameters of 0.510 to 1.510 inches are made
in one piece, without the hardened bushing. Gauges
ranging in diameter from 1.510 to 5.510 inches are
made with a flange, as shown in figure 3-56, which
reduces the weight and makes them easier to handle.
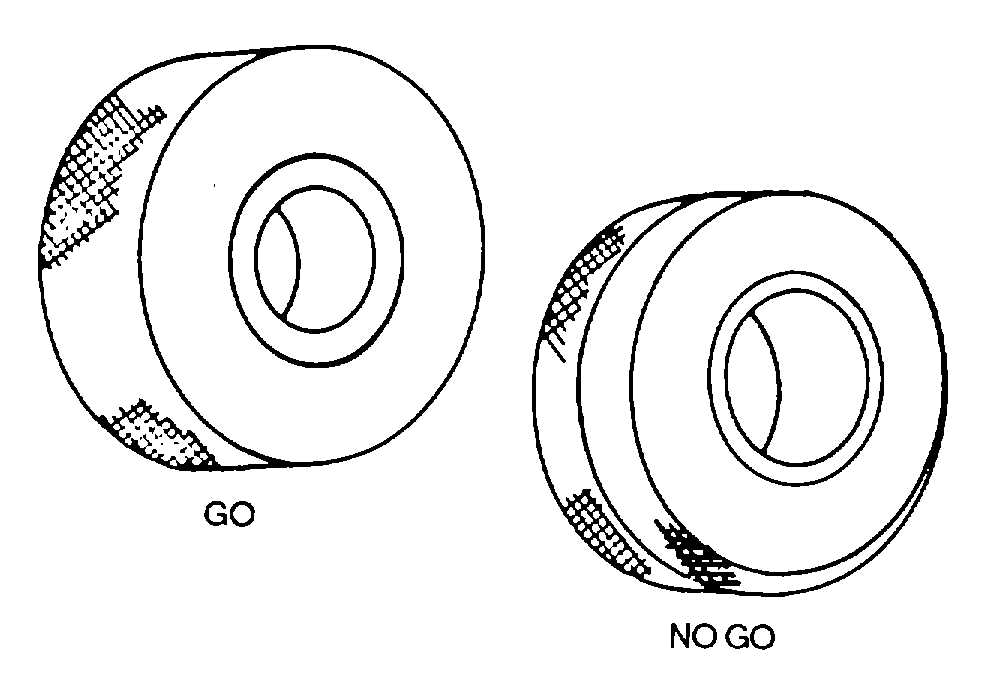
There are two types of ring gauges; the GO and the NO
GO gauges (see figure 3-57).
(1)
GO ring gauges. GO ring gauges are
larger than NO GO gauges. The outer surface of the
ring is knurled.
Figure 3-55. Ring Gauges
Figure 3-56. Flanged Ring Gauge
Figure 3-57. Ring Gauge Types
3-25