TM 1-1500-204-23-9
a.
Operation. Height gauges usually have vernier
scales, and are operated similarly to depth gauges, as
outlined in paragraph 3-11b(2). The clamping screws
ensure that the measuring arm will not slip after the
gauge is removed from the object being measured.
b.
Care. Observe the following practices for the
care and upkeep of height gauges:
(1)
Coat all metal parts of height gauges with
a light coat of oil to prevent rust.
(2)
Carefully store height gauges in separate
containers provided by manufacturer.
(3)
Keep graduations and markings clean and
legible.
(4)
Do not drop any height gauge. Small
nicks
and
scratches
can
cause
inaccurate
measurements.
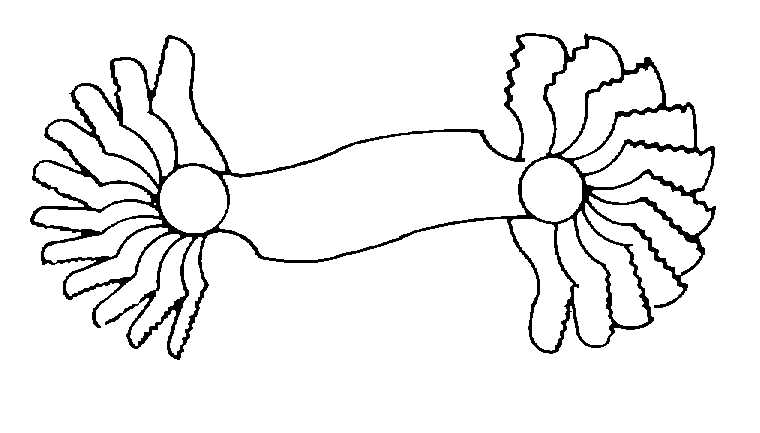
3-13. Thread Gauges. Thread gauges are used to
determine the pitch and number of threads per inch on
threaded fasteners. They consist of leaves whose
edges are toothed to correspond to standard threads. A
typical thread gauge is shown in figure 3-52.
Figure 3-52. Thread Gauge
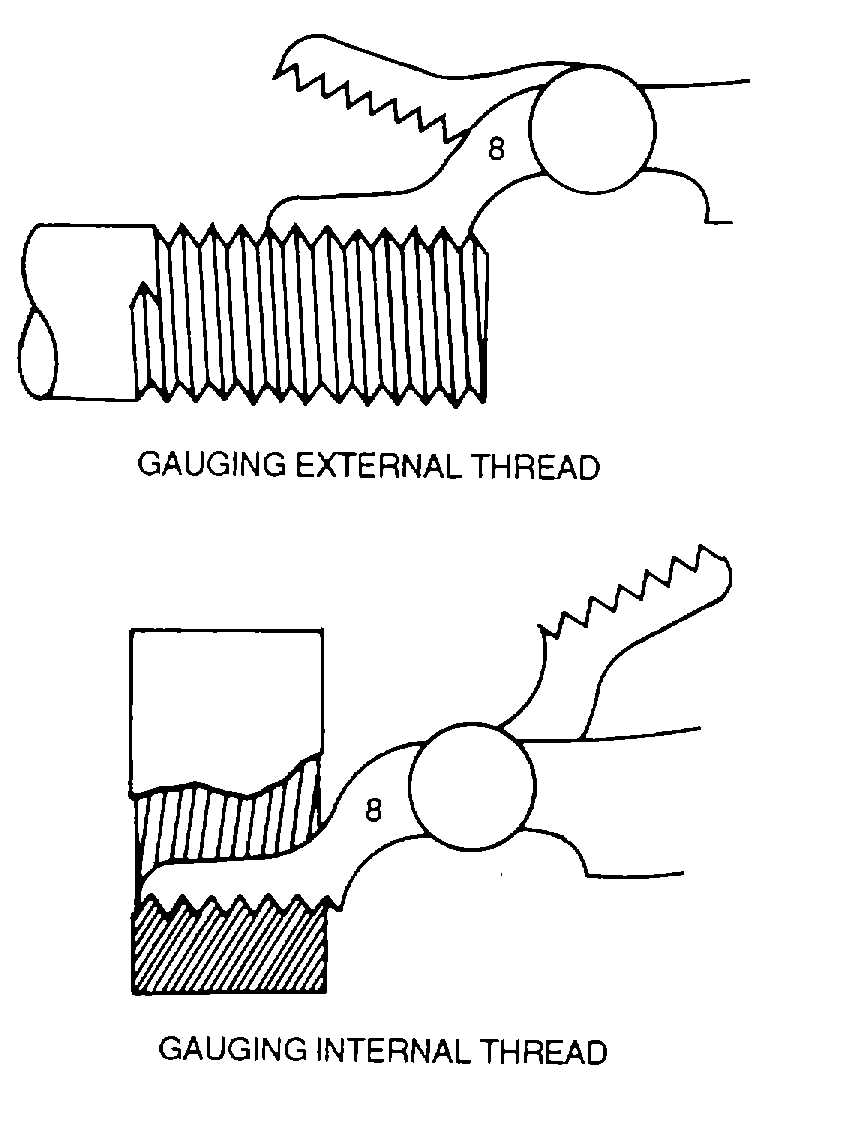
a.
Use. To measure the unknown pitch of a
thread, compare it with the standard of the thread
gauge. Various leaves are held to the threads until an
exact fit is found, as shown in figure 3-53.
b.
Reading. The number of threads per inch is
indicated on the leaf which is found to exactly match the
threads being measured. Using this value as a basis,
correct sizes of nuts, bolts, screws, taps, and dies are
selected for use.
c.
Care. Observe the following practices for the
care and upkeep of thread gauges:
Figure 3-53. Using Thread Gauges
(1)
Coat metal parts of thread gauges with a
light film of oil to prevent rust.
(2)
Store gauges in separate containers.
(3)
Keep graduations and markings clean and
legible.
(4)
Do not drop thread gauges. Small nicks
and scratches will result in inaccurate measurements.
3-14. Plug Gauges. Thread gauges provide a fast and
reliable method of determining whether internal and
external threads match. One disadvantage of their use
is that part of the thread tolerance must be built into the
thread gauge. For more precise measurement of thread
pitch, plug gauges are used.
a.
Use. GO and NO GO plug gauges are used to
inspect internal threads. They are available as separate
tools or with both ends combined in one tool, as shown
in figure 3-54. Threads are inspected as follows:
(1)
GO gauge. For an internal thread to be
accepted, the GO plug gauge must pass through the
entire length of the thread.
3-24