TM 1-1500-204-23-9
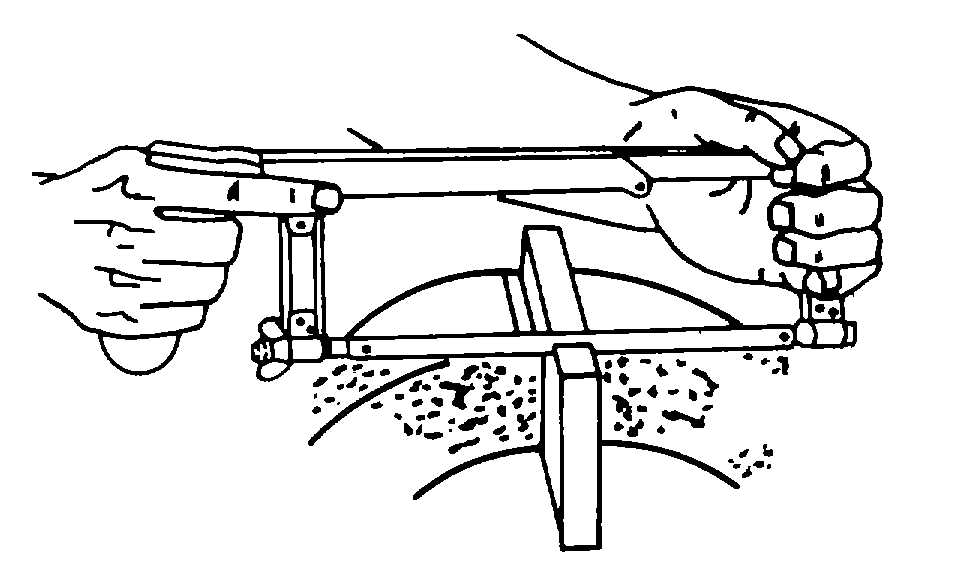
Figure 4-100. Proper Way to Hold a Hacksaw
a.
Taps. Taps are used for cutting inside or
female threads.
(1)
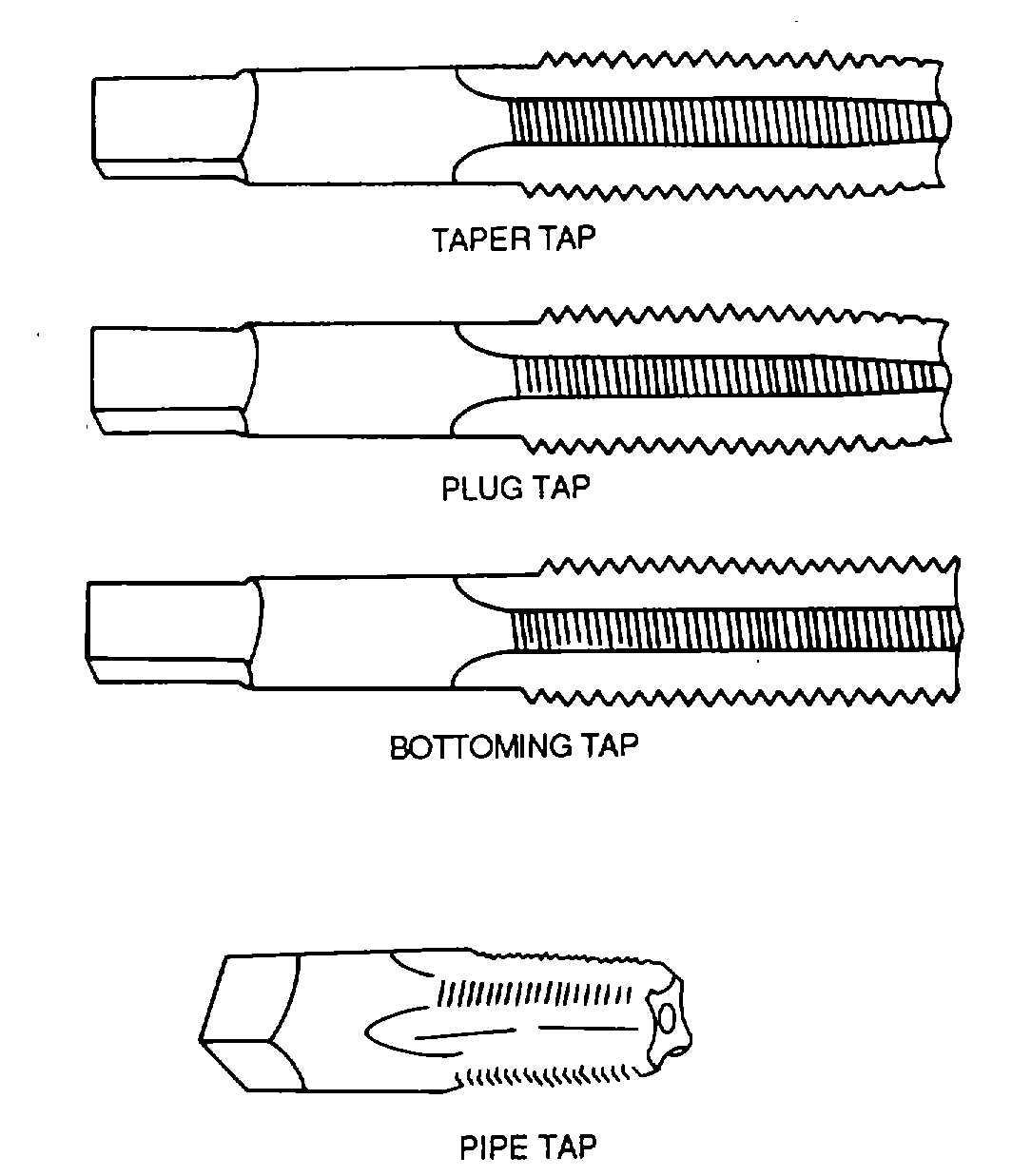
Types. The four types of taps are the
taper, plug, bottoming, and pipe taps, as shown in figure
4-101.
(a)
Taper tap. The taper tap has a chamfer
length of 8 to 10 threads. This tap is used to start all
threads and to tap through holes.
(b)
Plug tap. Plug taps have a chamfer
length of 3 to 5 threads and are used when one end of
the hole is closed, but a full thread is not required all the
way to the bottom of the hole.
(c)
Bottoming tap. The bottoming tap is used
for cutting a full thread to the bottom of a closed hole.
(d)
Pipe tap. Pipe taps are used for pipe
fittings, grease fittings, and other places where an
extremely tight fit is necessary. The tap diameter tapers
at the rate of 3/4 inch per foot.
(2)
Use. The following paragraphs outline the
procedures for the use of taps:
(a)
The hole that is to be tapped must be of
the correct size. Figure 4-102 shows a drill and wire
gauge index which gives the correct drill sizes for
specific sizes and threads of taps.
(b)
After the hole is drilled, the tap (held by
the tap wrench) is placed in the hole.
Figure 4-101. Taps
WARNING
Dry-cleaning solvent is flammable
and solvent vapors are toxic. Use
P-D-680, Type II Solvent in a
well-ventilated area. Keep away
from
open
flames.
Avoid
prolonged solvent contact with
skin.
NOTE
*
Plug
taps
or
bottoming
taps
should never be used to start a
thread.
*
The wrench should be held in the
center when starting the tap, and
light pressure should be applied
for the first two or three turns.
(c)
Apply a cutting oil or lubricant from table
4-3 which corresponds to the type of metal being
tapped.
4-39