TM 1-1500-204-23-1
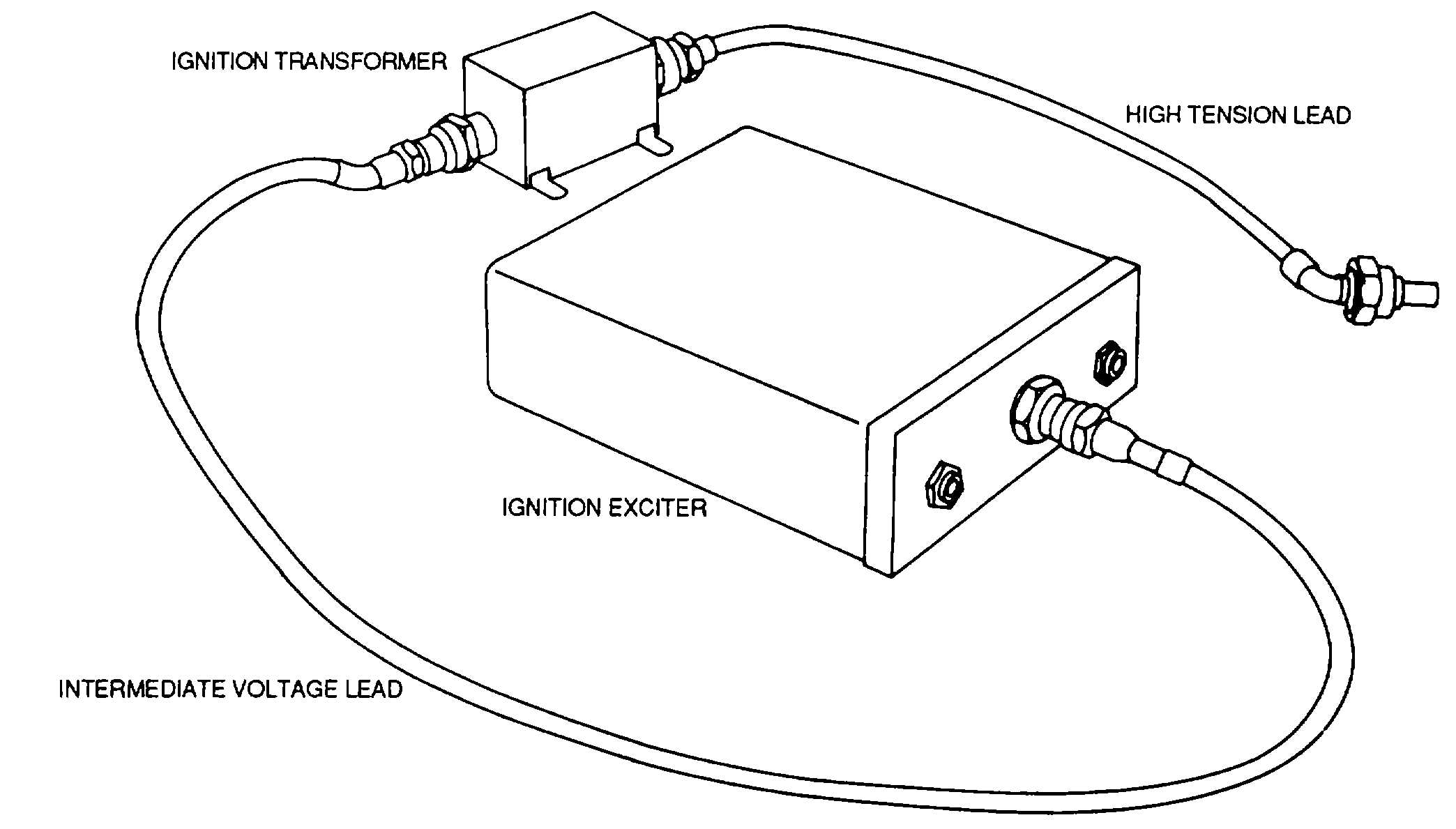
Figure 8-13. One Side of a Typical Ignition System
(1) Fuel controls. Regardless of the type, all fuel
controls accomplish essentially the same functions, but
some sense more engine variables than others. The
fuel control senses power lever position, engine rpm,
either compressor inlet pressure or temperature, and
burner pressure or compressor discharge pressure.
These variables affect the amount of thrust that an
engine will produce for a given fuel flow.
(2) Fuel nozzles. The fuel nozzles inject fuel into
the combustion area In a highly atomized, precisely
patterned spray so that burning is completed evenly and
in the shortest possible time and in the smallest possible
space. Fuel nozzle types vary considerably between
engines, although for the most part fuel is sprayed into
the combustion area under pressure through small
orifice in the nozzles The two types of fuel nozzles
generally used are the simplex and the duplex
configurations.
(a) Simplex fuel nozzle. The simplex fuel nozzle
was the first type nozzle used in turbine engines and
was replaced in most installations with the duplex
nozzle, which gave better atomization at starting and
idling speeds. The simplex nozzle, as shown in figure 8-
15, is still being used to a limited degree. Each of the
simplex nozzles consists of a nozzle tip, an insert, and a
strainer made up of fine-mesh screen and a support.
(b) Duplex fuel nozzle. The duplex fuel nozzle is
the nozzle most widely used in present-day gas turbine
engines The duplex nozzle usually requires a dual
manifold and a pressurizing valve or flow divider for
dividing primary and main fuel flow into a desirable
spray pattern for combustion over a wide range of
operating pressures. A nozzle typical of this type is
shown In figure 8-16.
(3) Fuel filters. A low-pressure filter Is installed
between the supply tanks and the engine fuel system to
protect the engine-driven fuel pump and various control
devices. An additional high-pressure fuel filter is
installed between the fuel pump and the fuel control to
protect the fuel control from contaminants. The three
most common types of filters in use are the micron filter,
the wafer screen filter, and the plain screen mesh filter.
The individual use of each of these filters is dictated by
the filtering treatment required at a particular location.
8-6. Turbine Engine Inspection and Maintenance.
Turbine engines shall be Inspected and maintained in
accordance with the applicable maintenance manual.
General procedures for various components and
systems are explained in the following paragraphs.
8-11