TM 1-1500-204-23-9
Figure 4-78. Drawfiling
e.
Handle Installation. A file should never be used
without a firmly attached handle. The following
paragraphs describe the installation and removal
procedures for file handles.
(1)
Installation. Handles are installed on files
as follows:
(a)
Select a handle that will fit the tang
snugly.
(b)
Wet the tang with water and insert it into
the handle.
CAUTION
Never hammer a file into its handle,
because the tang can bend or the file
can break.
(c)
Tap the end of the handle on a flat
surface until the file is properly seated.
(2)
Removal.
To
remove
the
handle,
proceed as follows:
(a)
Hold the file with the left hand and the
handle with the right hand.
(b)
Pull the file from the handle while rapping
the ferrule end of the handle against the
edge of a bench.
f.
Care. Observe the following practices for the
care and upkeep of files:
(1)
Break in a new file as discussed in
paragraph 4-11d(1).
(2)
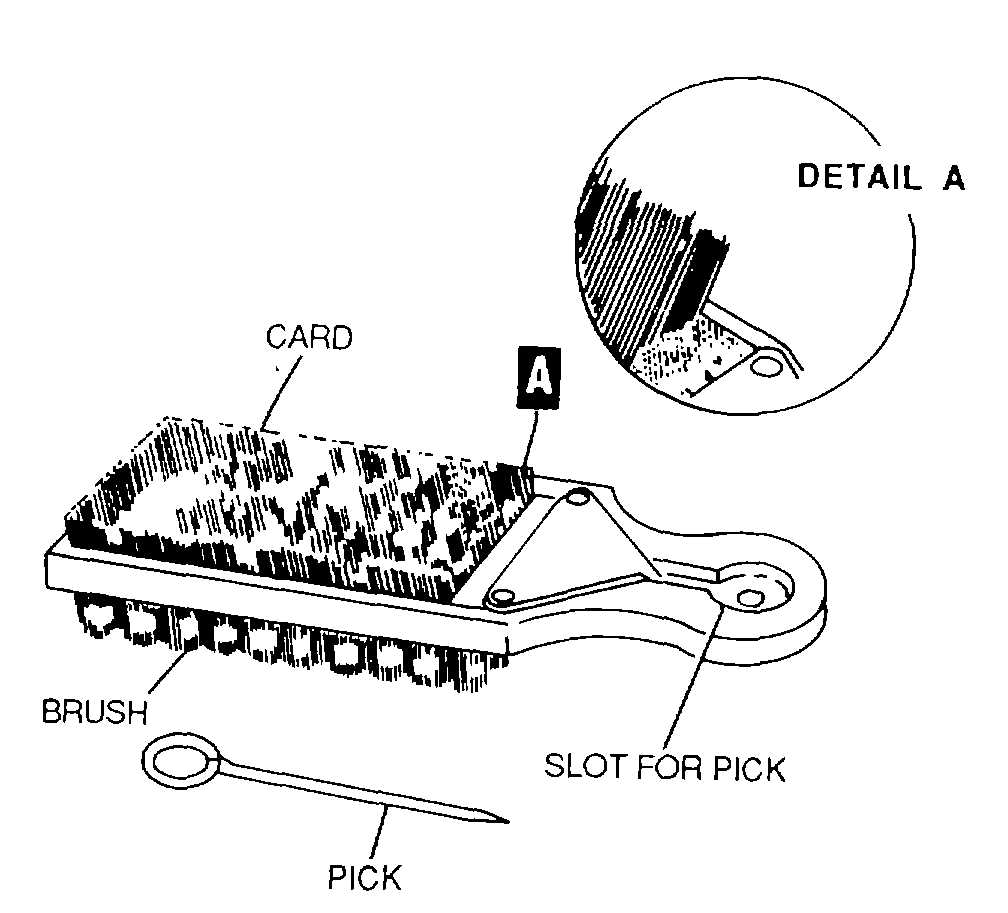
Clean files using the file cleaner shown in
figure 4-79.
(3)
Never strike the file against a vise or
other object to remove filings. Use the file cleaner.
(4)
Do not oil files. This will cause the file to
slide across the work, preventing efficient cutting.
(5)
Wrap each file in a waterproofed barrier
wrapping paper. Place the files in racks or boxes so that
the faces or edges of the files will not touch each other.
Figure 4-79. File Cleaner
4-12. Hand Drills. Hand drills are used when electric
or pneumatic power is not available. These drills
provide a somewhat slower drilling speed because they
are hand-powered.
a.
Types. There are two types of hand drills used
in Army aircraft maintenance. They are the breast, and
hand drills.
(1)
Breast drill. The breast drill has a base
for the user to lean against while using the drill. It has a
speed shifter which provides a means of selecting low or
high drill speeds. The low drill speed has a 1:1 gear
ratio, and the high speed ratio is 3-1/2:1. This drill,
shown in figure 4-80, is used to drill holes in wood,
plastic, and small gauge sheet metal.
(2)
Hand drill. The hand drill, shown in figure
4-81, has a handle to provide pressure by hand. This
drill is used to drill holes in wood and sheet metal, and
4-28