TM 1-1500-204-23-9
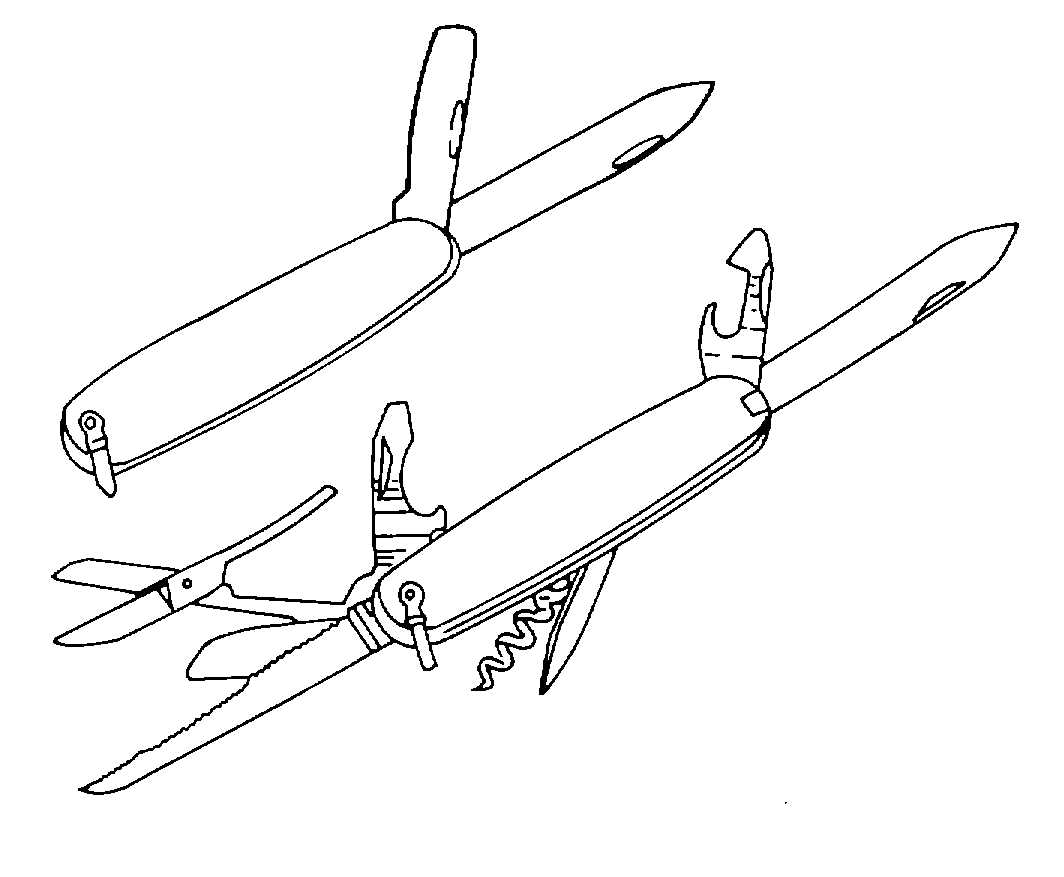
Figure 4-51. Pocket Knives
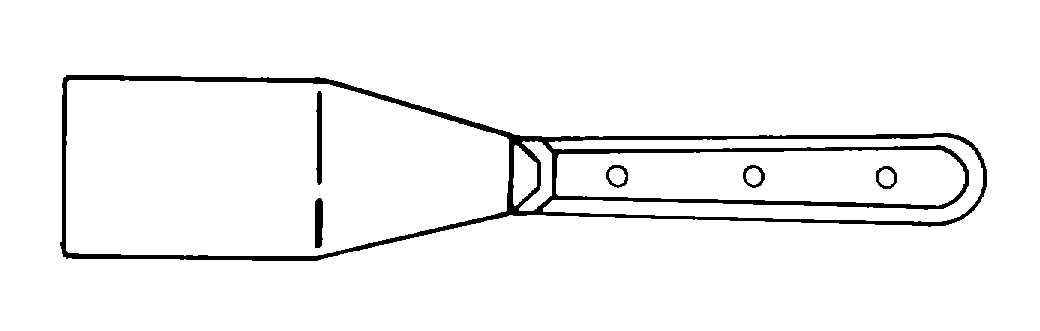
Figure 4-52. Putty Knife
•
Do not use knives which are larger than can be
handled safely to cut the work.
•
Use knives only for the purpose for which they
were designed.
•
Always cut away from the hands and body.
•
Do not carry open knives in pockets.
•
Do not leave knives in such a position that they
will cause injury to others.
c.
Care. Observe the following practices for the
care and upkeep of knives:
(1)
Sharpen blades by stroking them with an
oilstone moistened with a few drops of engine oil, MIL-L-
6082.
(2)
Store
knives
in
sheaths
or
other
containers to prevent the cutting edges from contacting
other
hard
objects.
(3)
Lightly coat all metal parts with a thin film
of oil to prevent rust.
(4)
For long-term storage, apply a thin film of
rust-preventive compound on all metal parts and store in
a dry place.
4-8. Clamping Devices. Vises and clamps are used to
hold objects being worked to a definite size and shape.
The objects must be held firmly while the work is being
performed. The bench vise and the carriage clamp are
the clamping devices most widely used in aircraft
maintenance.
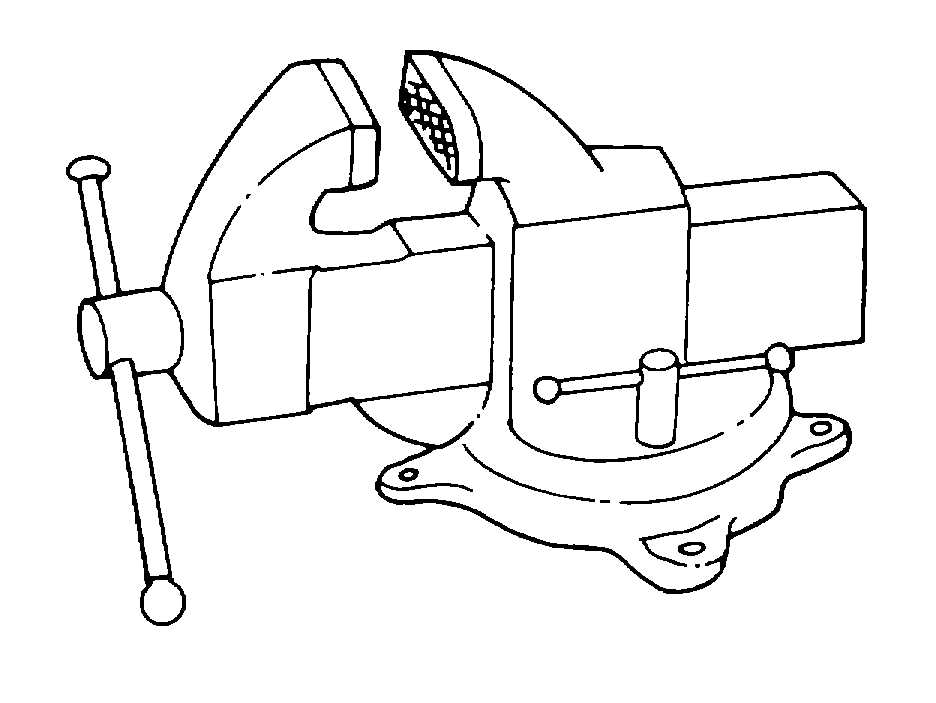
a.
Bench Vise. The bench vise, shown in figure 4-
53, is a large steel vise with rough jaws that prevent the
work from slipping. Most vises of this type have a
swivel base so that the upper portion can be rotated.
The bench vise is usually bolt-mounted onto a bench.
Figure 4-53. Bench Vise
(1)
Use.
The
following
steps
are
general
procedures for using a bench vise:
WARNING
Ensure that the vise is bolted securely to
a bench or table and that the swivel base
is locked before using. Failure to comply
may result in the vise falling off the
surface
and
causing
damage
to
equipment and injury to personnel.
(a)
Open the jaws of the vise wide enough to
insert the object to be held.
4-18